Keep only essential files: sources, headers, build system, and licenses.
+++ /dev/null
-aho-corasick
-==
-
-Aho-Corasick parallel string search, using interleaved arrays.
-
-Mischa Sandberg mischasan@gmail.com
-
-ACISM is an implementation of Aho-Corasick parallel string search,
-using an Interleaved State-transition Matrix.
-It combines the fastest possible Aho-Corasick implementation,
-with the smallest possible data structure (!).
-
-FEATURES
---------
-
-* Fast. No hashing, no tree traversal; just a straight look-up equivalent to
- matrix[state, input-byte] per input character.
-
-* Tiny. On average, the whole data structure (mostly the array) takes about 2-3 bytes per
- input pattern byte. The original set of pattern strings can be reverse-generated from the machine.
-
-* Shareable. The state machine contains no pointers, so it can be compiled once,
- then memory-mapped by many processes.
-
-* Searches byte vectors, not null-terminated strings.
- Suitable for searching machine code as much as searching text.
-
-* DOS-proof. Well, that's an attribute of Aho-Corasick,
- so no real points for that.
-
-* Stream-ready. The state can be saved between calls to search data.
-
-DOCUMENTATION
--------------
-
-The GoogleDocs description is at http://goo.gl/lE6zG
-I originally called it "psearch", but found that name was overused by other authors.
-
-LICENSE
--------
-
-Though I've had strong suggestions to go with BSD license, I'm going with GPL2 until I figure out
-how to keep in touch with people who download and use the code. Hence the "CONTACT ME IF..." line in the license.
-
-GETTING STARTED
----------------
-
-Download the source, type "gmake".
-"gmake install" exports lib/libacism.a, include/acism.h and bin/acism_x.
-"acism_x.c" is a good example of calling acism_create and acism_scan/acism_more.
-
-(If you're interested in the GNUmakefile and rules.mk,
- check my blog posts on non-recursive make, at mischasan.wordpress.com.)
-
-HISTORY
--------
-
-The interleaved-array approach was tried and discarded in the late 70's, because the compile time was O(n^2).
-acism_create beats the problem with a "hint" array that tracks the restart points for searches.
-That, plus discarding the original idea of how to get maximal density, resulted in the tiny-fast win-win.
-
-ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
-----------------
-
-I'd like to thank Mike Shannon, who wanted to see a machine built to make best use of L1/L2 cache.
-The change to do that doubled performance on hardware with a much larger cache than the matrix.
-Go figure.
+++ /dev/null
-<p align="center"><img src="scripts/data/logo/logo_1.svg"></p>
-<b>
-<table>
- <tr>
- <td>
- master branch
- </td>
- <td>
- Windows <a href="https://ci.appveyor.com/project/onqtam/doctest/branch/master"><img src="https://ci.appveyor.com/api/projects/status/j89qxtahyw1dp4gd/branch/master?svg=true"></a>
- </td>
- <td>
- All <a href="https://github.com/onqtam/doctest/actions?query=branch%3Amaster"><img src="https://github.com/onqtam/doctest/workflows/CI/badge.svg?branch=master"></a>
- </td>
- <td>
- <a href="https://coveralls.io/github/onqtam/doctest?branch=master"><img src="https://coveralls.io/repos/github/onqtam/doctest/badge.svg?branch=master"></a>
- </td>
- <!--
- <td>
- <a href="https://scan.coverity.com/projects/onqtam-doctest"><img src="https://scan.coverity.com/projects/7865/badge.svg"></a>
- </td>
- -->
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>
- dev branch
- </td>
- <td>
- Windows <a href="https://ci.appveyor.com/project/onqtam/doctest/branch/dev"><img src="https://ci.appveyor.com/api/projects/status/j89qxtahyw1dp4gd/branch/dev?svg=true"></a>
- </td>
- <td>
- All <a href="https://github.com/onqtam/doctest/actions?query=branch%3Adev"><img src="https://github.com/onqtam/doctest/workflows/CI/badge.svg?branch=dev"></a>
- </td>
- <td>
- <a href="https://coveralls.io/github/onqtam/doctest?branch=dev"><img src="https://coveralls.io/repos/github/onqtam/doctest/badge.svg?branch=dev"></a>
- </td>
- <!--
- <td>
- </td>
- -->
- </tr>
-</table>
-</b>
-
-**doctest** is a new C++ testing framework but is by far the fastest both in compile times (by [**orders of magnitude**](doc/markdown/benchmarks.md)) and runtime compared to other feature-rich alternatives. It brings the ability of compiled languages such as [**D**](https://dlang.org/spec/unittest.html) / [**Rust**](https://doc.rust-lang.org/book/second-edition/ch11-00-testing.html) / [**Nim**](https://nim-lang.org/docs/unittest.html) to have tests written directly in the production code thanks to a fast, transparent and flexible test runner with a clean interface.
-
-[](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C%2B%2B#Standardization)
-[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
-[](https://github.com/onqtam/doctest/releases)
-[](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/onqtam/doctest/master/doctest/doctest.h)
-[](https://bestpractices.coreinfrastructure.org/projects/503)
-[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/onqtam/doctest/context:cpp)
-[](https://gitter.im/onqtam/doctest?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge)
-[](https://wandbox.org/permlink/nJIibfbivG7BG7r1)
-<!--
-[](https://isocpp.org/)
-[](https://github.com/onqtam/doctest/blob/master/doc/markdown/readme.md#reference)
--->
-
-[<img src="https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/8225057/5990484/70413560-a9ab-11e4-8942-1a63607c0b00.png" align="right">](http://www.patreon.com/onqtam)
-
-The framework is and will stay free but needs your support to sustain its development. There are lots of <a href="doc/markdown/roadmap.md"><b>new features</b></a> and maintenance to do. If you work for a company using **doctest** or have the means to do so, please consider financial support. Monthly donations via Patreon and one-offs via PayPal.
-
-[<img src="https://www.paypalobjects.com/en_US/i/btn/btn_donate_LG.gif" align="right">](https://www.paypal.me/onqtam/10)
-
-A complete example with a self-registering test that compiles to an executable looks like this:
-
-
-
-There are many C++ testing frameworks - [Catch](https://github.com/catchorg/Catch2), [Boost.Test](http://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_64_0/libs/test/doc/html/index.html), [UnitTest++](https://github.com/unittest-cpp/unittest-cpp), [cpputest](https://github.com/cpputest/cpputest), [googletest](https://github.com/google/googletest) and many [other](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_unit_testing_frameworks#C.2B.2B).
-
-The **key** differences between it and other testing frameworks are that it is light and unintrusive:
-- Ultra light on compile times both in terms of [**including the header**](doc/markdown/benchmarks.md#cost-of-including-the-header) and writing [**thousands of asserts**](doc/markdown/benchmarks.md#cost-of-an-assertion-macro)
-- Doesn't produce any warnings even on the [**most aggressive**](scripts/cmake/common.cmake#L84) warning levels for **MSVC**/**GCC**/**Clang**
-- Offers a way to remove **everything** testing-related from the binary with the [**```DOCTEST_CONFIG_DISABLE```**](doc/markdown/configuration.md#doctest_config_disable) identifier
-- [**thread-safe**](doc/markdown/faq.md#is-doctest-thread-aware) - asserts (and logging) can be used from multiple threads spawned from a single test case - [**example**](examples/all_features/concurrency.cpp)
-- asserts can be used [**outside of a testing context**](doc/markdown/assertions.md#using-asserts-out-of-a-testing-context) - as a general purpose assert library - [**example**](examples/all_features/asserts_used_outside_of_tests.cpp)
-- Doesn't pollute the global namespace (everything is in namespace ```doctest```) and doesn't drag **any** headers with it
-- Very [**portable**](doc/markdown/features.md#extremely-portable) C++11 (use tag [**1.2.9**](https://github.com/onqtam/doctest/tree/1.2.9) for C++98) with over 180 different CI builds (static analysis, sanitizers...)
-- binaries (exe/dll) can use the test runner of another binary - so tests end up in a single registry - [**example**](examples/executable_dll_and_plugin/)
-
-
-
-This allows the framework to be used in more ways than any other - tests can be written directly in the production code!
-
-*Tests can be considered a form of documentation and should be able to reside near the production code which they test.*
-
-- This makes the barrier for writing tests **much lower** - you don't have to: **1)** make a separate source file **2)** include a bunch of stuff in it **3)** add it to the build system and **4)** add it to source control - You can just write the tests for a class or a piece of functionality at the bottom of its source file - or even header file!
-- Tests in the production code can be thought of as documentation or up-to-date comments - showing the use of APIs
-- Testing internals that are not exposed through the public API and headers is no longer a mind-bending exercise
-- [**Test-driven development**](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Test-driven_development) in C++ has never been easier!
-
-The framework can be used like any other if you don't want/need to mix production code and tests - check out the [**features**](doc/markdown/features.md).
-
-**doctest** is modeled after [**Catch**](https://github.com/catchorg/Catch2) and some parts of the code have been taken directly - check out [**the differences**](doc/markdown/faq.md#how-is-doctest-different-from-catch).
-
-[This table](https://github.com/martinmoene/catch-lest-other-comparison) compares **doctest** / [**Catch**](https://github.com/catchorg/Catch2) / [**lest**](https://github.com/martinmoene/lest) which are all very similar.
-
-Checkout the [**CppCon 2017 talk**](https://cppcon2017.sched.com/event/BgsI/mix-tests-and-production-code-with-doctest-implementing-and-using-the-fastest-modern-c-testing-framework) on [**YouTube**](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eH1CxEC29l8) to get a better understanding of how the framework works and read about how to use it in [**the JetBrains article**](https://blog.jetbrains.com/rscpp/better-ways-testing-with-doctest/) - highlighting the unique aspects of the framework! On a short description on how to use the framework along production code you could refer to [**this GitHub issue**](https://github.com/onqtam/doctest/issues/252). There is also an [**older article**](https://accu.org/var/uploads/journals/Overload137.pdf) in the february edition of ACCU Overload 2017.
-
-[](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eH1CxEC29l8)
-
-Documentation
--------------
-
-Project:
-
-- [Features and design goals](doc/markdown/features.md) - the complete list of features
-- [Roadmap](doc/markdown/roadmap.md) - upcoming features
-- [Benchmarks](doc/markdown/benchmarks.md) - compile-time and runtime supremacy
-- [Contributing](CONTRIBUTING.md) - how to make a proper pull request
-- [Changelog](CHANGELOG.md) - generated changelog based on closed issues/PRs
-
-Usage:
-
-- [Tutorial](doc/markdown/tutorial.md) - make sure you have read it before the other parts of the documentation
-- [Assertion macros](doc/markdown/assertions.md)
-- [Test cases, subcases and test fixtures](doc/markdown/testcases.md)
-- [Parameterized test cases](doc/markdown/parameterized-tests.md)
-- [Command line](doc/markdown/commandline.md)
-- [Logging macros](doc/markdown/logging.md)
-- [```main()``` entry point](doc/markdown/main.md)
-- [Configuration](doc/markdown/configuration.md)
-- [String conversions](doc/markdown/stringification.md)
-- [Reporters](doc/markdown/reporters.md)
-- [Extensions](doc/markdown/extensions.md)
-- [FAQ](doc/markdown/faq.md)
-- [Build systems](doc/markdown/build-systems.md)
-- [Examples](examples)
-
-Contributing
-------------
-
-[<img src="https://cloud.githubusercontent.com/assets/8225057/5990484/70413560-a9ab-11e4-8942-1a63607c0b00.png" align="right">](http://www.patreon.com/onqtam)
-
-Support the development of the project with donations! There is a list of planned features which are all important and big - see the [**roadmap**](doc/markdown/roadmap.md). I took a break from working in the industry to make open source software so every cent is a big deal.
-
-[<img src="https://www.paypalobjects.com/en_US/i/btn/btn_donate_LG.gif" align="right">](https://www.paypal.me/onqtam/10)
-
-If you work for a company using **doctest** or have the means to do so, please consider financial support.
-
-Contributions in the form of issues and pull requests are welcome as well - check out the [**Contributing**](CONTRIBUTING.md) page.
-
-Stargazers over time
-------------
-
-[](https://starcharts.herokuapp.com/onqtam/doctest)
-
-Logo
-------------
-
-The [logo](scripts/data/logo) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Copyright © 2019 [area55git](https://github.com/area55git) [](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
-
-<p align="center"><img src="scripts/data/logo/icon_2.svg"></p>
+++ /dev/null
-2.4.11
\ No newline at end of file
+++ /dev/null
-FEATURES
-1) Support new http-protocol (/checkv2)
-2) Return action, symbols, symbol options, messages, scan time
-
-INSTALL
-
-1) Get cJSON.c, cJSON.h, put to dlfunc src dir (https://github.com/DaveGamble/cJSON)
-2) Compile dlfunc library:
- cc rspamd.c -fPIC -fpic -shared -I/root/rpmbuild/BUILD/exim-4.89/build-Linux-x86_64/ -o exim-rspamd-http-dlfunc.so
-3) See exim-example.txt for exim configure
+++ /dev/null
-acl_smtp_data = acl_check_data
-
-.....
-
-acl_check_data:
-
-.....
-
-# RSPAMD: START
- warn
- !authenticated = *
- add_header = X-Spam-Checker-Version: Rspamd
- add_header = :at_start:Authentication-Results: ip=$sender_host_address:$sender_host_port, host=$sender_host_name, helo=$sender_helo_name, mailfrom=$sender_address
- warn
- #spam = nobody:true
- #set acl_m0_rspamd = $spam_report
- set acl_m0_rspamd = ${dlfunc{/usr/local/libexec/exim/exim-rspamd-http-dlfunc.so}{rspamd}{/var/run/rspamd/rspamd.sock}{defer_ok}}
- accept
- authenticated = *
- warn
- condition = ${if eq{$acl_m0_rspamd}{}}
- logwrite = RSPAMD check failed
- add_header = X-Spam-Info: Check failed
- warn
- condition = ${if match{$acl_m0_rspamd}{\N^rspamd dlfunc:\s*\N}{yes}{no}}
- logwrite = RSPAMD check defer: ${sg{$acl_m0_rspamd}{\N^rspamd dlfunc:\s*\N}{}}
- add_header = X-Spam-Info: Check deffered
-
- warn
- remove_header = X-Spam-Checker-Version:X-Spam-Status:X-Spam-Info:X-Spam-Result
- set acl_m1 = No
- warn
- condition = ${if !eq{$acl_m0_rspamd}{}}
- set acl_m1_yesno = ${if match{$acl_m0_rspamd}{\NAction: (.+?)\n\N}{$1}{}}
- set acl_m2_status = ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{reject}{REJECT}{\
- ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{add header}{PROBABLY}{\
- ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{rewrite subject}{PROBABLY}{\
- ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{soft reject}{SOFT}{\
- ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{greylist}{GREYLIST}{NO}}\
- }}\
- }}\
- }}\
- }}
- set acl_m1_yesno = ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{}{unknown}{\
- ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{reject}{Yes}{\
- ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{add header}{Yes}{\
- ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{rewrite subject}{Yes}{\
- ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{soft reject}{Probably}{\
- ${if eq{$acl_m1_yesno}{greylist}{Probably}{No}}\
- }}\
- }}\
- }}\
- }}\
- }}
- #logwrite = RSPAMD: status: $acl_m2_status
- #logwrite = RSPAMD DEBUG: $acl_m0_rspamd
- set acl_m0_rspamd = ${sg{$acl_m0_rspamd}{ Action:.+\n}{}}
- warn
- condition = ${if !eq{$acl_m0_rspamd}{}}
- logwrite = RSPAMD: $acl_m2_status, $acl_m0_rspamd
- add_header = X-Spam-Result: $acl_m0_rspamd
- add_header = X-Spam-Status: $acl_m1_yesno
- defer
- condition = ${if eq{$acl_m2_status}{GREYLIST}}
- log_message = Rspamd $acl_m2_status
- message = Try again later. Message greylisted
- defer
- condition = ${if eq{$acl_m2_status}{SOFT}}
- log_message = Rspamd $acl_m2_status
- message = Try again later. Message previously greylisted
- deny
- condition = ${if eq{$acl_m2_status}{REJECT}}
- log_message = Rspamd $acl_m2_status
- message = This message detected as SPAM and rejected
-# RSPAMD: END
+++ /dev/null
-<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/156254208-f5b743a9-88cf-439d-b0c0-923d53e8d551.png" alt="{fmt}" width="25%"/>
-
-[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Alinux)
-[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Amacos)
-[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Awindows)
-[](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?\%0Acolspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20\%0ASummary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
-[](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt)
-[](https://securityscorecards.dev/viewer/?uri=github.com/fmtlib/fmt)
-
-**{fmt}** is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe
-alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams.
-
-If you like this project, please consider donating to one of the funds
-that help victims of the war in Ukraine: <https://www.stopputin.net/>.
-
-[Documentation](https://fmt.dev)
-
-[Cheat Sheets](https://hackingcpp.com/cpp/libs/fmt.html)
-
-Q&A: ask questions on [StackOverflow with the tag
-fmt](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt).
-
-Try {fmt} in [Compiler Explorer](https://godbolt.org/z/8Mx1EW73v).
-
-# Features
-
-- Simple [format API](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html) with positional
- arguments for localization
-- Implementation of [C++20
- std::format](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/format) and
- [C++23 std::print](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/io/print)
-- [Format string syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html) similar
- to Python\'s
- [format](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format)
-- Fast IEEE 754 floating-point formatter with correct rounding,
- shortness and round-trip guarantees using the
- [Dragonbox](https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox) algorithm
-- Portable Unicode support
-- Safe [printf
- implementation](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#printf-formatting)
- including the POSIX extension for positional arguments
-- Extensibility: [support for user-defined
- types](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#formatting-user-defined-types)
-- High performance: faster than common standard library
- implementations of `(s)printf`, iostreams, `to_string` and
- `to_chars`, see [Speed tests](#speed-tests) and [Converting a
- hundred million integers to strings per
- second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html)
-- Small code size both in terms of source code with the minimum
- configuration consisting of just three files, `core.h`, `format.h`
- and `format-inl.h`, and compiled code; see [Compile time and code
- bloat](#compile-time-and-code-bloat)
-- Reliability: the library has an extensive set of
- [tests](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/tree/master/test) and is
- [continuously fuzzed](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?colspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20Summary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
-- Safety: the library is fully type-safe, errors in format strings can
- be reported at compile time, automatic memory management prevents
- buffer overflow errors
-- Ease of use: small self-contained code base, no external
- dependencies, permissive MIT
- [license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE.rst)
-- [Portability](https://fmt.dev/latest/index.html#portability) with
- consistent output across platforms and support for older compilers
-- Clean warning-free codebase even on high warning levels such as
- `-Wall -Wextra -pedantic`
-- Locale independence by default
-- Optional header-only configuration enabled with the
- `FMT_HEADER_ONLY` macro
-
-See the [documentation](https://fmt.dev) for more details.
-
-# Examples
-
-**Print to stdout** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Tevcjh))
-
-``` c++
-#include <fmt/core.h>
-
-int main() {
- fmt::print("Hello, world!\n");
-}
-```
-
-**Format a string** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/oK8h33))
-
-``` c++
-std::string s = fmt::format("The answer is {}.", 42);
-// s == "The answer is 42."
-```
-
-**Format a string using positional arguments**
-([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Yn7Txe))
-
-``` c++
-std::string s = fmt::format("I'd rather be {1} than {0}.", "right", "happy");
-// s == "I'd rather be happy than right."
-```
-
-**Print dates and times** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/c31ExdY3W))
-
-``` c++
-#include <fmt/chrono.h>
-
-int main() {
- auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
- fmt::print("Date and time: {}\n", now);
- fmt::print("Time: {:%H:%M}\n", now);
-}
-```
-
-Output:
-
- Date and time: 2023-12-26 19:10:31.557195597
- Time: 19:10
-
-**Print a container** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/MxM1YqjE7))
-
-``` c++
-#include <vector>
-#include <fmt/ranges.h>
-
-int main() {
- std::vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3};
- fmt::print("{}\n", v);
-}
-```
-
-Output:
-
- [1, 2, 3]
-
-**Check a format string at compile time**
-
-``` c++
-std::string s = fmt::format("{:d}", "I am not a number");
-```
-
-This gives a compile-time error in C++20 because `d` is an invalid
-format specifier for a string.
-
-**Write a file from a single thread**
-
-``` c++
-#include <fmt/os.h>
-
-int main() {
- auto out = fmt::output_file("guide.txt");
- out.print("Don't {}", "Panic");
-}
-```
-
-This can be [5 to 9 times faster than
-fprintf](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/08/04/optimal-file-buffer-size.html).
-
-**Print with colors and text styles**
-
-``` c++
-#include <fmt/color.h>
-
-int main() {
- fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::crimson) | fmt::emphasis::bold,
- "Hello, {}!\n", "world");
- fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::floral_white) | bg(fmt::color::slate_gray) |
- fmt::emphasis::underline, "Olá, {}!\n", "Mundo");
- fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::steel_blue) | fmt::emphasis::italic,
- "你好{}!\n", "世界");
-}
-```
-
-Output on a modern terminal with Unicode support:
-
-
-
-# Benchmarks
-
-## Speed tests
-
-| Library | Method | Run Time, s |
-|-------------------|---------------|-------------|
-| libc | printf | 0.91 |
-| libc++ | std::ostream | 2.49 |
-| {fmt} 9.1 | fmt::print | 0.74 |
-| Boost Format 1.80 | boost::format | 6.26 |
-| Folly Format | folly::format | 1.87 |
-
-{fmt} is the fastest of the benchmarked methods, \~20% faster than
-`printf`.
-
-The above results were generated by building `tinyformat_test.cpp` on
-macOS 12.6.1 with `clang++ -O3 -DNDEBUG -DSPEED_TEST -DHAVE_FORMAT`, and
-taking the best of three runs. In the test, the format string
-`"%0.10f:%04d:%+g:%s:%p:%c:%%\n"` or equivalent is filled 2,000,000
-times with output sent to `/dev/null`; for further details refer to the
-[source](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/src/tinyformat-test.cc).
-
-{fmt} is up to 20-30x faster than `std::ostringstream` and `sprintf` on
-IEEE754 `float` and `double` formatting
-([dtoa-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark)) and faster
-than [double-conversion](https://github.com/google/double-conversion)
-and [ryu](https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu):
-
-[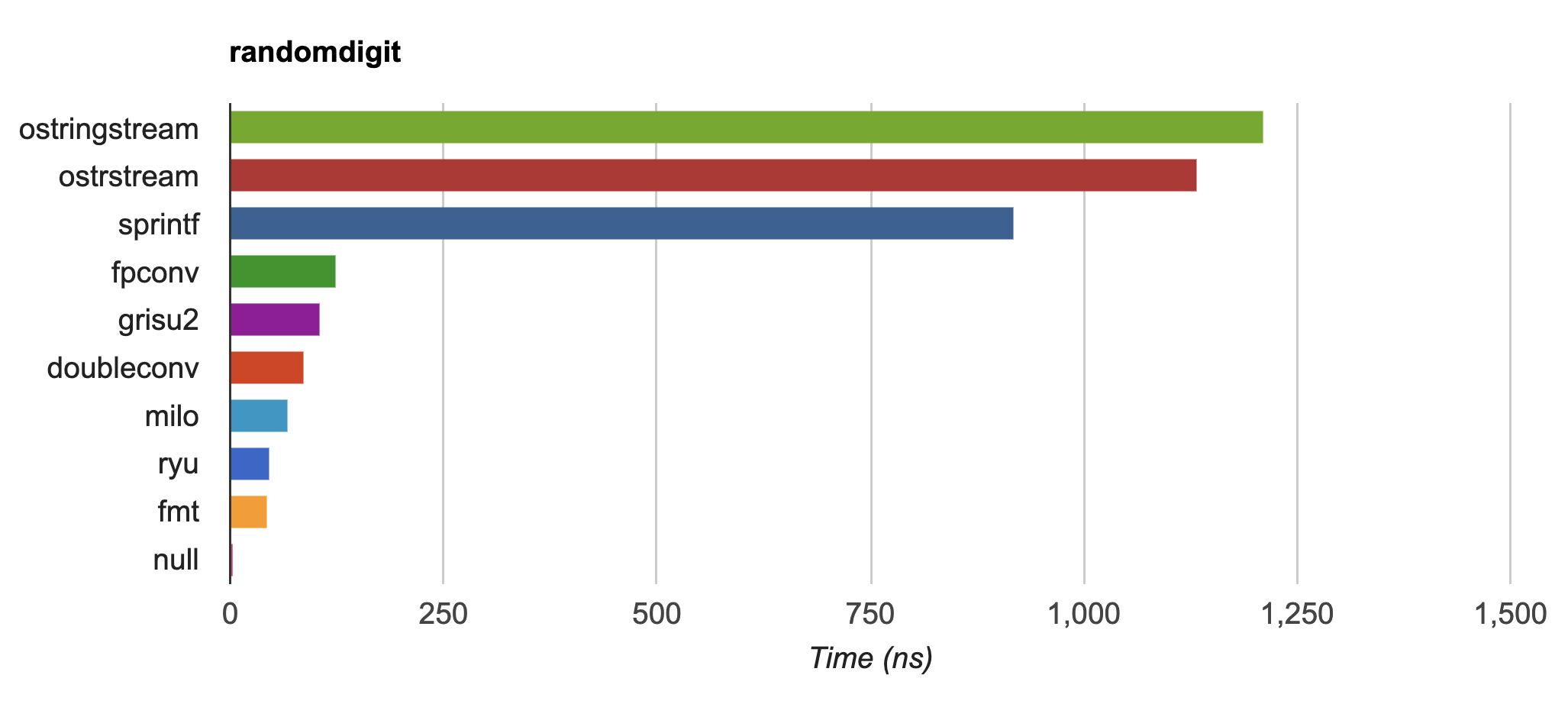](https://fmt.dev/unknown_mac64_clang12.0.html)
-
-## Compile time and code bloat
-
-The script [bloat-test.py][test] from [format-benchmark][bench] tests compile
-time and code bloat for nontrivial projects. It generates 100 translation units
-and uses `printf()` or its alternative five times in each to simulate a
-medium-sized project. The resulting executable size and compile time (Apple
-clang version 15.0.0 (clang-1500.1.0.2.5), macOS Sonoma, best of three) is shown
-in the following tables.
-
-[test]: https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/bloat-test.py
-[bench]: https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark
-
-**Optimized build (-O3)**
-
-| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
-|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
-| printf | 1.6 | 54 | 50 |
-| IOStreams | 25.9 | 98 | 84 |
-| fmt 83652df | 4.8 | 54 | 50 |
-| tinyformat | 29.1 | 161 | 136 |
-| Boost Format | 55.0 | 530 | 317 |
-
-{fmt} is fast to compile and is comparable to `printf` in terms of per-call
-binary size (within a rounding error on this system).
-
-**Non-optimized build**
-
-| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
-|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
-| printf | 1.4 | 54 | 50 |
-| IOStreams | 23.4 | 92 | 68 |
-| {fmt} 83652df | 4.4 | 89 | 85 |
-| tinyformat | 24.5 | 204 | 161 |
-| Boost Format | 36.4 | 831 | 462 |
-
-`libc`, `lib(std)c++`, and `libfmt` are all linked as shared libraries
-to compare formatting function overhead only. Boost Format is a
-header-only library so it doesn\'t provide any linkage options.
-
-## Running the tests
-
-Please refer to [Building the
-library](https://fmt.dev/latest/usage.html#building-the-library) for
-instructions on how to build the library and run the unit tests.
-
-Benchmarks reside in a separate repository,
-[format-benchmarks](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark), so to
-run the benchmarks you first need to clone this repository and generate
-Makefiles with CMake:
-
- $ git clone --recursive https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark.git
- $ cd format-benchmark
- $ cmake .
-
-Then you can run the speed test:
-
- $ make speed-test
-
-or the bloat test:
-
- $ make bloat-test
-
-# Migrating code
-
-[clang-tidy](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/) v18 provides the
-[modernize-use-std-print](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/checks/modernize/use-std-print.html)
-check that is capable of converting occurrences of `printf` and
-`fprintf` to `fmt::print` if configured to do so. (By default it
-converts to `std::print`.)
-
-# Notable projects using this library
-
-- [0 A.D.](https://play0ad.com/): a free, open-source, cross-platform
- real-time strategy game
-- [AMPL/MP](https://github.com/ampl/mp): an open-source library for
- mathematical programming
-- [Apple's FoundationDB](https://github.com/apple/foundationdb): an open-source,
- distributed, transactional key-value store
-- [Aseprite](https://github.com/aseprite/aseprite): animated sprite
- editor & pixel art tool
-- [AvioBook](https://www.aviobook.aero/en): a comprehensive aircraft
- operations suite
-- [Blizzard Battle.net](https://battle.net/): an online gaming
- platform
-- [Celestia](https://celestia.space/): real-time 3D visualization of
- space
-- [Ceph](https://ceph.com/): a scalable distributed storage system
-- [ccache](https://ccache.dev/): a compiler cache
-- [ClickHouse](https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse): an
- analytical database management system
-- [Contour](https://github.com/contour-terminal/contour/): a modern
- terminal emulator
-- [CUAUV](https://cuauv.org/): Cornell University\'s autonomous
- underwater vehicle
-- [Drake](https://drake.mit.edu/): a planning, control, and analysis
- toolbox for nonlinear dynamical systems (MIT)
-- [Envoy](https://lyft.github.io/envoy/): C++ L7 proxy and
- communication bus (Lyft)
-- [FiveM](https://fivem.net/): a modification framework for GTA V
-- [fmtlog](https://github.com/MengRao/fmtlog): a performant
- fmtlib-style logging library with latency in nanoseconds
-- [Folly](https://github.com/facebook/folly): Facebook open-source
- library
-- [GemRB](https://gemrb.org/): a portable open-source implementation
- of Bioware's Infinity Engine
-- [Grand Mountain
- Adventure](https://store.steampowered.com/app/1247360/Grand_Mountain_Adventure/):
- a beautiful open-world ski & snowboarding game
-- [HarpyWar/pvpgn](https://github.com/pvpgn/pvpgn-server): Player vs
- Player Gaming Network with tweaks
-- [KBEngine](https://github.com/kbengine/kbengine): an open-source
- MMOG server engine
-- [Keypirinha](https://keypirinha.com/): a semantic launcher for
- Windows
-- [Kodi](https://kodi.tv/) (formerly xbmc): home theater software
-- [Knuth](https://kth.cash/): high-performance Bitcoin full-node
-- [libunicode](https://github.com/contour-terminal/libunicode/): a
- modern C++17 Unicode library
-- [MariaDB](https://mariadb.org/): relational database management
- system
-- [Microsoft Verona](https://github.com/microsoft/verona): research
- programming language for concurrent ownership
-- [MongoDB](https://mongodb.com/): distributed document database
-- [MongoDB Smasher](https://github.com/duckie/mongo_smasher): a small
- tool to generate randomized datasets
-- [OpenSpace](https://openspaceproject.com/): an open-source
- astrovisualization framework
-- [PenUltima Online (POL)](https://www.polserver.com/): an MMO server,
- compatible with most Ultima Online clients
-- [PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch): an open-source
- machine learning library
-- [quasardb](https://www.quasardb.net/): a distributed,
- high-performance, associative database
-- [Quill](https://github.com/odygrd/quill): asynchronous low-latency
- logging library
-- [QKW](https://github.com/ravijanjam/qkw): generalizing aliasing to
- simplify navigation, and execute complex multi-line terminal
- command sequences
-- [redis-cerberus](https://github.com/HunanTV/redis-cerberus): a Redis
- cluster proxy
-- [redpanda](https://vectorized.io/redpanda): a 10x faster Kafka®
- replacement for mission-critical systems written in C++
-- [rpclib](http://rpclib.net/): a modern C++ msgpack-RPC server and
- client library
-- [Salesforce Analytics
- Cloud](https://www.salesforce.com/analytics-cloud/overview/):
- business intelligence software
-- [Scylla](https://www.scylladb.com/): a Cassandra-compatible NoSQL
- data store that can handle 1 million transactions per second on a
- single server
-- [Seastar](http://www.seastar-project.org/): an advanced, open-source
- C++ framework for high-performance server applications on modern
- hardware
-- [spdlog](https://github.com/gabime/spdlog): super fast C++ logging
- library
-- [Stellar](https://www.stellar.org/): financial platform
-- [Touch Surgery](https://www.touchsurgery.com/): surgery simulator
-- [TrinityCore](https://github.com/TrinityCore/TrinityCore):
- open-source MMORPG framework
-- [🐙 userver framework](https://userver.tech/): open-source
- asynchronous framework with a rich set of abstractions and database
- drivers
-- [Windows Terminal](https://github.com/microsoft/terminal): the new
- Windows terminal
-
-[More\...](https://github.com/search?q=fmtlib&type=Code)
-
-If you are aware of other projects using this library, please let me
-know by [email](mailto:victor.zverovich@gmail.com) or by submitting an
-[issue](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues).
-
-# Motivation
-
-So why yet another formatting library?
-
-There are plenty of methods for doing this task, from standard ones like
-the printf family of function and iostreams to Boost Format and
-FastFormat libraries. The reason for creating a new library is that
-every existing solution that I found either had serious issues or
-didn\'t provide all the features I needed.
-
-## printf
-
-The good thing about `printf` is that it is pretty fast and readily
-available being a part of the C standard library. The main drawback is
-that it doesn\'t support user-defined types. `printf` also has safety
-issues although they are somewhat mitigated with [\_\_attribute\_\_
-((format (printf,
-\...))](https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Function-Attributes.html) in
-GCC. There is a POSIX extension that adds positional arguments required
-for
-[i18n](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internationalization_and_localization)
-to `printf` but it is not a part of C99 and may not be available on some
-platforms.
-
-## iostreams
-
-The main issue with iostreams is best illustrated with an example:
-
-``` c++
-std::cout << std::setprecision(2) << std::fixed << 1.23456 << "\n";
-```
-
-which is a lot of typing compared to printf:
-
-``` c++
-printf("%.2f\n", 1.23456);
-```
-
-Matthew Wilson, the author of FastFormat, called this \"chevron hell\".
-iostreams don\'t support positional arguments by design.
-
-The good part is that iostreams support user-defined types and are safe
-although error handling is awkward.
-
-## Boost Format
-
-This is a very powerful library that supports both `printf`-like format
-strings and positional arguments. Its main drawback is performance.
-According to various benchmarks, it is much slower than other methods
-considered here. Boost Format also has excessive build times and severe
-code bloat issues (see [Benchmarks](#benchmarks)).
-
-## FastFormat
-
-This is an interesting library that is fast, safe and has positional
-arguments. However, it has significant limitations, citing its author:
-
-> Three features that have no hope of being accommodated within the
-> current design are:
->
-> - Leading zeros (or any other non-space padding)
-> - Octal/hexadecimal encoding
-> - Runtime width/alignment specification
-
-It is also quite big and has a heavy dependency, on STLSoft, which might be
-too restrictive for use in some projects.
-
-## Boost Spirit.Karma
-
-This is not a formatting library but I decided to include it here for
-completeness. As iostreams, it suffers from the problem of mixing
-verbatim text with arguments. The library is pretty fast, but slower on
-integer formatting than `fmt::format_to` with format string compilation
-on Karma\'s own benchmark, see [Converting a hundred million integers to
-strings per
-second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html).
-
-# License
-
-{fmt} is distributed under the MIT
-[license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE).
-
-# Documentation License
-
-The [Format String Syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html) section
-in the documentation is based on the one from Python [string module
-documentation](https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html#module-string).
-For this reason, the documentation is distributed under the Python
-Software Foundation license available in
-[doc/python-license.txt](https://raw.github.com/fmtlib/fmt/master/doc/python-license.txt).
-It only applies if you distribute the documentation of {fmt}.
-
-# Maintainers
-
-The {fmt} library is maintained by Victor Zverovich
-([vitaut](https://github.com/vitaut)) with contributions from many other
-people. See
-[Contributors](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/graphs/contributors) and
-[Releases](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases) for some of the
-names. Let us know if your contribution is not listed or mentioned
-incorrectly and we\'ll make it right.
-
-# Security Policy
-
-To report a security issue, please disclose it at [security
-advisory](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/security/advisories/new).
-
-This project is maintained by a team of volunteers on a
-reasonable-effort basis. As such, please give us at least *90* days to
-work on a fix before public exposure.
+++ /dev/null
-serge-sans-paille <sguelton@quarkslab.com>
-Jérôme Dumesnil <jerome.dumesnil@gmail.com>
-Chris Beck <chbeck@tesla.com>
+++ /dev/null
-[](https://travis-ci.org/redis/hiredis)
-
-# HIREDIS
-
-Hiredis is a minimalistic C client library for the [Redis](http://redis.io/) database.
-
-It is minimalistic because it just adds minimal support for the protocol, but
-at the same time it uses a high level printf-alike API in order to make it
-much higher level than otherwise suggested by its minimal code base and the
-lack of explicit bindings for every Redis command.
-
-Apart from supporting sending commands and receiving replies, it comes with
-a reply parser that is decoupled from the I/O layer. It
-is a stream parser designed for easy reusability, which can for instance be used
-in higher level language bindings for efficient reply parsing.
-
-Hiredis only supports the binary-safe Redis protocol, so you can use it with any
-Redis version >= 1.2.0.
-
-The library comes with multiple APIs. There is the
-*synchronous API*, the *asynchronous API* and the *reply parsing API*.
-
-## UPGRADING
-
-Version 0.9.0 is a major overhaul of hiredis in every aspect. However, upgrading existing
-code using hiredis should not be a big pain. The key thing to keep in mind when
-upgrading is that hiredis >= 0.9.0 uses a `redisContext*` to keep state, in contrast to
-the stateless 0.0.1 that only has a file descriptor to work with.
-
-## Synchronous API
-
-To consume the synchronous API, there are only a few function calls that need to be introduced:
-
-```c
-redisContext *redisConnect(const char *ip, int port);
-void *redisCommand(redisContext *c, const char *format, ...);
-void freeReplyObject(void *reply);
-```
-
-### Connecting
-
-The function `redisConnect` is used to create a so-called `redisContext`. The
-context is where Hiredis holds state for a connection. The `redisContext`
-struct has an integer `err` field that is non-zero when the connection is in
-an error state. The field `errstr` will contain a string with a description of
-the error. More information on errors can be found in the **Errors** section.
-After trying to connect to Redis using `redisConnect` you should
-check the `err` field to see if establishing the connection was successful:
-```c
-redisContext *c = redisConnect("127.0.0.1", 6379);
-if (c != NULL && c->err) {
- printf("Error: %s\n", c->errstr);
- // handle error
-}
-```
-
-### Sending commands
-
-There are several ways to issue commands to Redis. The first that will be introduced is
-`redisCommand`. This function takes a format similar to printf. In the simplest form,
-it is used like this:
-```c
-reply = redisCommand(context, "SET foo bar");
-```
-
-The specifier `%s` interpolates a string in the command, and uses `strlen` to
-determine the length of the string:
-```c
-reply = redisCommand(context, "SET foo %s", value);
-```
-When you need to pass binary safe strings in a command, the `%b` specifier can be
-used. Together with a pointer to the string, it requires a `size_t` length argument
-of the string:
-```c
-reply = redisCommand(context, "SET foo %b", value, (size_t) valuelen);
-```
-Internally, Hiredis splits the command in different arguments and will
-convert it to the protocol used to communicate with Redis.
-One or more spaces separates arguments, so you can use the specifiers
-anywhere in an argument:
-```c
-reply = redisCommand(context, "SET key:%s %s", myid, value);
-```
-
-### Using replies
-
-The return value of `redisCommand` holds a reply when the command was
-successfully executed. When an error occurs, the return value is `NULL` and
-the `err` field in the context will be set (see section on **Errors**).
-Once an error is returned the context cannot be reused and you should set up
-a new connection.
-
-The standard replies that `redisCommand` are of the type `redisReply`. The
-`type` field in the `redisReply` should be used to test what kind of reply
-was received:
-
-* **`REDIS_REPLY_STATUS`**:
- * The command replied with a status reply. The status string can be accessed using `reply->str`.
- The length of this string can be accessed using `reply->len`.
-
-* **`REDIS_REPLY_ERROR`**:
- * The command replied with an error. The error string can be accessed identical to `REDIS_REPLY_STATUS`.
-
-* **`REDIS_REPLY_INTEGER`**:
- * The command replied with an integer. The integer value can be accessed using the
- `reply->integer` field of type `long long`.
-
-* **`REDIS_REPLY_NIL`**:
- * The command replied with a **nil** object. There is no data to access.
-
-* **`REDIS_REPLY_STRING`**:
- * A bulk (string) reply. The value of the reply can be accessed using `reply->str`.
- The length of this string can be accessed using `reply->len`.
-
-* **`REDIS_REPLY_ARRAY`**:
- * A multi bulk reply. The number of elements in the multi bulk reply is stored in
- `reply->elements`. Every element in the multi bulk reply is a `redisReply` object as well
- and can be accessed via `reply->element[..index..]`.
- Redis may reply with nested arrays but this is fully supported.
-
-Replies should be freed using the `freeReplyObject()` function.
-Note that this function will take care of freeing sub-reply objects
-contained in arrays and nested arrays, so there is no need for the user to
-free the sub replies (it is actually harmful and will corrupt the memory).
-
-**Important:** the current version of hiredis (0.10.0) frees replies when the
-asynchronous API is used. This means you should not call `freeReplyObject` when
-you use this API. The reply is cleaned up by hiredis _after_ the callback
-returns. This behavior will probably change in future releases, so make sure to
-keep an eye on the changelog when upgrading (see issue #39).
-
-### Cleaning up
-
-To disconnect and free the context the following function can be used:
-```c
-void redisFree(redisContext *c);
-```
-This function immediately closes the socket and then frees the allocations done in
-creating the context.
-
-### Sending commands (cont'd)
-
-Together with `redisCommand`, the function `redisCommandArgv` can be used to issue commands.
-It has the following prototype:
-```c
-void *redisCommandArgv(redisContext *c, int argc, const char **argv, const size_t *argvlen);
-```
-It takes the number of arguments `argc`, an array of strings `argv` and the lengths of the
-arguments `argvlen`. For convenience, `argvlen` may be set to `NULL` and the function will
-use `strlen(3)` on every argument to determine its length. Obviously, when any of the arguments
-need to be binary safe, the entire array of lengths `argvlen` should be provided.
-
-The return value has the same semantic as `redisCommand`.
-
-### Pipelining
-
-To explain how Hiredis supports pipelining in a blocking connection, there needs to be
-understanding of the internal execution flow.
-
-When any of the functions in the `redisCommand` family is called, Hiredis first formats the
-command according to the Redis protocol. The formatted command is then put in the output buffer
-of the context. This output buffer is dynamic, so it can hold any number of commands.
-After the command is put in the output buffer, `redisGetReply` is called. This function has the
-following two execution paths:
-
-1. The input buffer is non-empty:
- * Try to parse a single reply from the input buffer and return it
- * If no reply could be parsed, continue at *2*
-2. The input buffer is empty:
- * Write the **entire** output buffer to the socket
- * Read from the socket until a single reply could be parsed
-
-The function `redisGetReply` is exported as part of the Hiredis API and can be used when a reply
-is expected on the socket. To pipeline commands, the only things that needs to be done is
-filling up the output buffer. For this cause, two commands can be used that are identical
-to the `redisCommand` family, apart from not returning a reply:
-```c
-void redisAppendCommand(redisContext *c, const char *format, ...);
-void redisAppendCommandArgv(redisContext *c, int argc, const char **argv, const size_t *argvlen);
-```
-After calling either function one or more times, `redisGetReply` can be used to receive the
-subsequent replies. The return value for this function is either `REDIS_OK` or `REDIS_ERR`, where
-the latter means an error occurred while reading a reply. Just as with the other commands,
-the `err` field in the context can be used to find out what the cause of this error is.
-
-The following examples shows a simple pipeline (resulting in only a single call to `write(2)` and
-a single call to `read(2)`):
-```c
-redisReply *reply;
-redisAppendCommand(context,"SET foo bar");
-redisAppendCommand(context,"GET foo");
-redisGetReply(context,&reply); // reply for SET
-freeReplyObject(reply);
-redisGetReply(context,&reply); // reply for GET
-freeReplyObject(reply);
-```
-This API can also be used to implement a blocking subscriber:
-```c
-reply = redisCommand(context,"SUBSCRIBE foo");
-freeReplyObject(reply);
-while(redisGetReply(context,&reply) == REDIS_OK) {
- // consume message
- freeReplyObject(reply);
-}
-```
-### Errors
-
-When a function call is not successful, depending on the function either `NULL` or `REDIS_ERR` is
-returned. The `err` field inside the context will be non-zero and set to one of the
-following constants:
-
-* **`REDIS_ERR_IO`**:
- There was an I/O error while creating the connection, trying to write
- to the socket or read from the socket. If you included `errno.h` in your
- application, you can use the global `errno` variable to find out what is
- wrong.
-
-* **`REDIS_ERR_EOF`**:
- The server closed the connection which resulted in an empty read.
-
-* **`REDIS_ERR_PROTOCOL`**:
- There was an error while parsing the protocol.
-
-* **`REDIS_ERR_OTHER`**:
- Any other error. Currently, it is only used when a specified hostname to connect
- to cannot be resolved.
-
-In every case, the `errstr` field in the context will be set to hold a string representation
-of the error.
-
-## Asynchronous API
-
-Hiredis comes with an asynchronous API that works easily with any event library.
-Examples are bundled that show using Hiredis with [libev](http://software.schmorp.de/pkg/libev.html)
-and [libevent](http://monkey.org/~provos/libevent/).
-
-### Connecting
-
-The function `redisAsyncConnect` can be used to establish a non-blocking connection to
-Redis. It returns a pointer to the newly created `redisAsyncContext` struct. The `err` field
-should be checked after creation to see if there were errors creating the connection.
-Because the connection that will be created is non-blocking, the kernel is not able to
-instantly return if the specified host and port is able to accept a connection.
-```c
-redisAsyncContext *c = redisAsyncConnect("127.0.0.1", 6379);
-if (c->err) {
- printf("Error: %s\n", c->errstr);
- // handle error
-}
-```
-
-The asynchronous context can hold a disconnect callback function that is called when the
-connection is disconnected (either because of an error or per user request). This function should
-have the following prototype:
-```c
-void(const redisAsyncContext *c, int status);
-```
-On a disconnect, the `status` argument is set to `REDIS_OK` when disconnection was initiated by the
-user, or `REDIS_ERR` when the disconnection was caused by an error. When it is `REDIS_ERR`, the `err`
-field in the context can be accessed to find out the cause of the error.
-
-The context object is always freed after the disconnect callback fired. When a reconnect is needed,
-the disconnect callback is a good point to do so.
-
-Setting the disconnect callback can only be done once per context. For subsequent calls it will
-return `REDIS_ERR`. The function to set the disconnect callback has the following prototype:
-```c
-int redisAsyncSetDisconnectCallback(redisAsyncContext *ac, redisDisconnectCallback *fn);
-```
-### Sending commands and their callbacks
-
-In an asynchronous context, commands are automatically pipelined due to the nature of an event loop.
-Therefore, unlike the synchronous API, there is only a single way to send commands.
-Because commands are sent to Redis asynchronously, issuing a command requires a callback function
-that is called when the reply is received. Reply callbacks should have the following prototype:
-```c
-void(redisAsyncContext *c, void *reply, void *privdata);
-```
-The `privdata` argument can be used to curry arbitrary data to the callback from the point where
-the command is initially queued for execution.
-
-The functions that can be used to issue commands in an asynchronous context are:
-```c
-int redisAsyncCommand(
- redisAsyncContext *ac, redisCallbackFn *fn, void *privdata,
- const char *format, ...);
-int redisAsyncCommandArgv(
- redisAsyncContext *ac, redisCallbackFn *fn, void *privdata,
- int argc, const char **argv, const size_t *argvlen);
-```
-Both functions work like their blocking counterparts. The return value is `REDIS_OK` when the command
-was successfully added to the output buffer and `REDIS_ERR` otherwise. Example: when the connection
-is being disconnected per user-request, no new commands may be added to the output buffer and `REDIS_ERR` is
-returned on calls to the `redisAsyncCommand` family.
-
-If the reply for a command with a `NULL` callback is read, it is immediately freed. When the callback
-for a command is non-`NULL`, the memory is freed immediately following the callback: the reply is only
-valid for the duration of the callback.
-
-All pending callbacks are called with a `NULL` reply when the context encountered an error.
-
-### Disconnecting
-
-An asynchronous connection can be terminated using:
-```c
-void redisAsyncDisconnect(redisAsyncContext *ac);
-```
-When this function is called, the connection is **not** immediately terminated. Instead, new
-commands are no longer accepted and the connection is only terminated when all pending commands
-have been written to the socket, their respective replies have been read and their respective
-callbacks have been executed. After this, the disconnection callback is executed with the
-`REDIS_OK` status and the context object is freed.
-
-### Hooking it up to event library *X*
-
-There are a few hooks that need to be set on the context object after it is created.
-See the `adapters/` directory for bindings to *libev* and *libevent*.
-
-## Reply parsing API
-
-Hiredis comes with a reply parsing API that makes it easy for writing higher
-level language bindings.
-
-The reply parsing API consists of the following functions:
-```c
-redisReader *redisReaderCreate(void);
-void redisReaderFree(redisReader *reader);
-int redisReaderFeed(redisReader *reader, const char *buf, size_t len);
-int redisReaderGetReply(redisReader *reader, void **reply);
-```
-The same set of functions are used internally by hiredis when creating a
-normal Redis context, the above API just exposes it to the user for a direct
-usage.
-
-### Usage
-
-The function `redisReaderCreate` creates a `redisReader` structure that holds a
-buffer with unparsed data and state for the protocol parser.
-
-Incoming data -- most likely from a socket -- can be placed in the internal
-buffer of the `redisReader` using `redisReaderFeed`. This function will make a
-copy of the buffer pointed to by `buf` for `len` bytes. This data is parsed
-when `redisReaderGetReply` is called. This function returns an integer status
-and a reply object (as described above) via `void **reply`. The returned status
-can be either `REDIS_OK` or `REDIS_ERR`, where the latter means something went
-wrong (either a protocol error, or an out of memory error).
-
-The parser limits the level of nesting for multi bulk payloads to 7. If the
-multi bulk nesting level is higher than this, the parser returns an error.
-
-### Customizing replies
-
-The function `redisReaderGetReply` creates `redisReply` and makes the function
-argument `reply` point to the created `redisReply` variable. For instance, if
-the response of type `REDIS_REPLY_STATUS` then the `str` field of `redisReply`
-will hold the status as a vanilla C string. However, the functions that are
-responsible for creating instances of the `redisReply` can be customized by
-setting the `fn` field on the `redisReader` struct. This should be done
-immediately after creating the `redisReader`.
-
-For example, [hiredis-rb](https://github.com/pietern/hiredis-rb/blob/master/ext/hiredis_ext/reader.c)
-uses customized reply object functions to create Ruby objects.
-
-### Reader max buffer
-
-Both when using the Reader API directly or when using it indirectly via a
-normal Redis context, the redisReader structure uses a buffer in order to
-accumulate data from the server.
-Usually this buffer is destroyed when it is empty and is larger than 16
-KiB in order to avoid wasting memory in unused buffers
-
-However when working with very big payloads destroying the buffer may slow
-down performances considerably, so it is possible to modify the max size of
-an idle buffer changing the value of the `maxbuf` field of the reader structure
-to the desired value. The special value of 0 means that there is no maximum
-value for an idle buffer, so the buffer will never get freed.
-
-For instance if you have a normal Redis context you can set the maximum idle
-buffer to zero (unlimited) just with:
-```c
-context->reader->maxbuf = 0;
-```
-This should be done only in order to maximize performances when working with
-large payloads. The context should be set back to `REDIS_READER_MAX_BUF` again
-as soon as possible in order to prevent allocation of useless memory.
-
-## AUTHORS
-
-Hiredis was written by Salvatore Sanfilippo (antirez at gmail) and
-Pieter Noordhuis (pcnoordhuis at gmail) and is released under the BSD license.
-Hiredis is currently maintained by Matt Stancliff (matt at genges dot com) and
-Jan-Erik Rediger (janerik at fnordig dot com)
+++ /dev/null
-# LIBUCL
-
-[](https://circleci.com/gh/vstakhov/libucl)
-[](https://scan.coverity.com/projects/4138)
-[](https://coveralls.io/github/vstakhov/libucl?branch=master)
-
-**Table of Contents** *generated with [DocToc](http://doctoc.herokuapp.com/)*
-
-- [Introduction](#introduction)
-- [Basic structure](#basic-structure)
-- [Improvements to the json notation](#improvements-to-the-json-notation)
- - [General syntax sugar](#general-syntax-sugar)
- - [Automatic arrays creation](#automatic-arrays-creation)
- - [Named keys hierarchy](#named-keys-hierarchy)
- - [Convenient numbers and booleans](#convenient-numbers-and-booleans)
-- [General improvements](#general-improvements)
- - [Comments](#comments)
- - [Macros support](#macros-support)
- - [Variables support](#variables-support)
- - [Multiline strings](#multiline-strings)
- - [Single quoted strings](#single-quoted-strings)
-- [Emitter](#emitter)
-- [Validation](#validation)
-- [Performance](#performance)
-- [Conclusion](#conclusion)
-
-## Introduction
-
-This document describes the main features and principles of the configuration
-language called `UCL` - universal configuration language.
-
-If you are looking for the libucl API documentation you can find it at [this page](doc/api.md).
-
-## Basic structure
-
-UCL is heavily infused by `nginx` configuration as the example of a convenient configuration
-system. However, UCL is fully compatible with `JSON` format and is able to parse json files.
-For example, you can write the same configuration in the following ways:
-
-* in nginx like:
-
-```nginx
-param = value;
-section {
- param = value;
- param1 = value1;
- flag = true;
- number = 10k;
- time = 0.2s;
- string = "something";
- subsection {
- host = {
- host = "hostname";
- port = 900;
- }
- host = {
- host = "hostname";
- port = 901;
- }
- }
-}
-```
-
-* or in JSON:
-
-```json
-{
- "param": "value",
- "param1": "value1",
- "flag": true,
- "subsection": {
- "host": [
- {
- "host": "hostname",
- "port": 900
- },
- {
- "host": "hostname",
- "port": 901
- }
- ]
- }
-}
-```
-
-## Improvements to the json notation.
-
-There are various things that make ucl configuration more convenient for editing than strict json:
-
-### General syntax sugar
-
-* Braces are not necessary to enclose a top object: it is automatically treated as an object:
-
-```json
-"key": "value"
-```
-is equal to:
-```json
-{"key": "value"}
-```
-
-* There is no requirement of quotes for strings and keys, moreover, `:` may be replaced `=` or even be skipped for objects:
-
-```nginx
-key = value;
-section {
- key = value;
-}
-```
-is equal to:
-```json
-{
- "key": "value",
- "section": {
- "key": "value"
- }
-}
-```
-
-* No commas mess: you can safely place a comma or semicolon for the last element in an array or an object:
-
-```json
-{
- "key1": "value",
- "key2": "value",
-}
-```
-### Automatic arrays creation
-
-* Non-unique keys in an object are allowed and are automatically converted to the arrays internally:
-
-```json
-{
- "key": "value1",
- "key": "value2"
-}
-```
-is converted to:
-```json
-{
- "key": ["value1", "value2"]
-}
-```
-
-### Named keys hierarchy
-
-UCL accepts named keys and organize them into objects hierarchy internally. Here is an example of this process:
-```nginx
-section "blah" {
- key = value;
-}
-section foo {
- key = value;
-}
-```
-
-is converted to the following object:
-
-```nginx
-section {
- blah {
- key = value;
- }
- foo {
- key = value;
- }
-}
-```
-
-Plain definitions may be more complex and contain more than a single level of nested objects:
-
-```nginx
-section "blah" "foo" {
- key = value;
-}
-```
-
-is presented as:
-
-```nginx
-section {
- blah {
- foo {
- key = value;
- }
- }
-}
-```
-
-### Convenient numbers and booleans
-
-* Numbers can have suffixes to specify standard multipliers:
- + `[kKmMgG]` - standard 10 base multipliers (so `1k` is translated to 1000)
- + `[kKmMgG]b` - 2 power multipliers (so `1kb` is translated to 1024)
- + `[s|min|d|w|y]` - time multipliers, all time values are translated to float number of seconds, for example `10min` is translated to 600.0 and `10ms` is translated to 0.01
-* Hexadecimal integers can be used by `0x` prefix, for example `key = 0xff`. However, floating point values can use decimal base only.
-* Booleans can be specified as `true` or `yes` or `on` and `false` or `no` or `off`.
-* It is still possible to treat numbers and booleans as strings by enclosing them in double quotes.
-
-## General improvements
-
-### Comments
-
-UCL supports different style of comments:
-
-* single line: `#`
-* multiline: `/* ... */`
-
-Multiline comments may be nested:
-```c
-# Sample single line comment
-/*
- some comment
- /* nested comment */
- end of comment
-*/
-```
-
-### Macros support
-
-UCL supports external macros both multiline and single line ones:
-```nginx
-.macro_name "sometext";
-.macro_name {
- Some long text
- ....
-};
-```
-
-Moreover, each macro can accept an optional list of arguments in braces. These
-arguments themselves are the UCL object that is parsed and passed to a macro as
-options:
-
-```nginx
-.macro_name(param=value) "something";
-.macro_name(param={key=value}) "something";
-.macro_name(.include "params.conf") "something";
-.macro_name(#this is multiline macro
-param = [value1, value2]) "something";
-.macro_name(key="()") "something";
-```
-
-UCL also provide a convenient `include` macro to load content from another files
-to the current UCL object. This macro accepts either path to file:
-
-```nginx
-.include "/full/path.conf"
-.include "./relative/path.conf"
-.include "${CURDIR}/path.conf"
-```
-
-or URL (if ucl is built with url support provided by either `libcurl` or `libfetch`):
-
- .include "http://example.com/file.conf"
-
-`.include` macro supports a set of options:
-
-* `try` (default: **false**) - if this option is `true` than UCL treats errors on loading of
-this file as non-fatal. For example, such a file can be absent but it won't stop the parsing
-of the top-level document.
-* `sign` (default: **false**) - if this option is `true` UCL loads and checks the signature for
-a file from path named `<FILEPATH>.sig`. Trusted public keys should be provided for UCL API after
-parser is created but before any configurations are parsed.
-* `glob` (default: **false**) - if this option is `true` UCL treats the filename as GLOB pattern and load
-all files that matches the specified pattern (normally the format of patterns is defined in `glob` manual page
-for your operating system). This option is meaningless for URL includes.
-* `url` (default: **true**) - allow URL includes.
-* `path` (default: empty) - A UCL_ARRAY of directories to search for the include file.
-Search ends after the first match, unless `glob` is true, then all matches are included.
-* `prefix` (default false) - Put included contents inside an object, instead
-of loading them into the root. If no `key` is provided, one is automatically generated based on each files basename()
-* `key` (default: <empty string>) - Key to load contents of include into. If
-the key already exists, it must be the correct type
-* `target` (default: object) - Specify if the `prefix` `key` should be an
-object or an array.
-* `priority` (default: 0) - specify priority for the include (see below).
-* `duplicate` (default: 'append') - specify policy of duplicates resolving:
- - `append` - default strategy, if we have new object of higher priority then it replaces old one, if we have new object with less priority it is ignored completely, and if we have two duplicate objects with the same priority then we have a multi-value key (implicit array)
- - `merge` - if we have object or array, then new keys are merged inside, if we have a plain object then an implicit array is formed (regardless of priorities)
- - `error` - create error on duplicate keys and stop parsing
- - `rewrite` - always rewrite an old value with new one (ignoring priorities)
-
-Priorities are used by UCL parser to manage the policy of objects rewriting during including other files
-as following:
-
-* If we have two objects with the same priority then we form an implicit array
-* If a new object has bigger priority then we overwrite an old one
-* If a new object has lower priority then we ignore it
-
-By default, the priority of top-level object is set to zero (lowest priority). Currently,
-you can define up to 16 priorities (from 0 to 15). Includes with bigger priorities will
-rewrite keys from the objects with lower priorities as specified by the policy.
-
-### Variables support
-
-UCL supports variables in input. Variables are registered by a user of the UCL parser and can be presented in the following forms:
-
-* `${VARIABLE}`
-* `$VARIABLE`
-
-UCL currently does not support nested variables. To escape variables one could use double dollar signs:
-
-* `$${VARIABLE}` is converted to `${VARIABLE}`
-* `$$VARIABLE` is converted to `$VARIABLE`
-
-However, if no valid variables are found in a string, no expansion will be performed (and `$$` thus remains unchanged). This may be a subject
-to change in future libucl releases.
-
-### Multiline strings
-
-UCL can handle multiline strings as well as single line ones. It uses shell/perl like notation for such objects:
-```
-key = <<EOD
-some text
-splitted to
-lines
-EOD
-```
-
-In this example `key` will be interpreted as the following string: `some text\nsplitted to\nlines`.
-Here are some rules for this syntax:
-
-* Multiline terminator must start just after `<<` symbols and it must consist of capital letters only (e.g. `<<eof` or `<< EOF` won't work);
-* Terminator must end with a single newline character (and no spaces are allowed between terminator and newline character);
-* To finish multiline string you need to include a terminator string just after newline and followed by a newline (no spaces or other characters are allowed as well);
-* The initial and the final newlines are not inserted to the resulting string, but you can still specify newlines at the beginning and at the end of a value, for example:
-
-```
-key <<EOD
-
-some
-text
-
-EOD
-```
-
-### Single quoted strings
-
-It is possible to use single quoted strings to simplify escaping rules. All values passed in single quoted strings are *NOT* escaped, with two exceptions: a single `'` character just before `\` character, and a newline character just after `\` character that is ignored.
-
-```
-key = 'value'; # Read as value
-key = 'value\n\'; # Read as value\n\
-key = 'value\''; # Read as value'
-key = 'value\
-bla'; # Read as valuebla
-```
-
-## Emitter
-
-Each UCL object can be serialized to one of the three supported formats:
-
-* `JSON` - canonic json notation (with spaces indented structure);
-* `Compacted JSON` - compact json notation (without spaces or newlines);
-* `Configuration` - nginx like notation;
-* `YAML` - yaml inlined notation.
-
-## Validation
-
-UCL allows validation of objects. It uses the same schema that is used for json: [json schema v4](http://json-schema.org). UCL supports the full set of json schema with the exception of remote references. This feature is unlikely useful for configuration objects. Of course, a schema definition can be in UCL format instead of JSON that simplifies schemas writing. Moreover, since UCL supports multiple values for keys in an object it is possible to specify generic integer constraints `maxValues` and `minValues` to define the limits of values count in a single key. UCL currently is not absolutely strict about validation schemas themselves, therefore UCL users should supply valid schemas (as it is defined in json-schema draft v4) to ensure that the input objects are validated properly.
-
-## Performance
-
-Are UCL parser and emitter fast enough? Well, there are some numbers.
-I got a 19Mb file that consist of ~700 thousand lines of json (obtained via
-http://www.json-generator.com/). Then I checked jansson library that performs json
-parsing and emitting and compared it with UCL. Here are results:
-
-```
-jansson: parsed json in 1.3899 seconds
-jansson: emitted object in 0.2609 seconds
-
-ucl: parsed input in 0.6649 seconds
-ucl: emitted config in 0.2423 seconds
-ucl: emitted json in 0.2329 seconds
-ucl: emitted compact json in 0.1811 seconds
-ucl: emitted yaml in 0.2489 seconds
-```
-
-So far, UCL seems to be significantly faster than jansson on parsing and slightly faster on emitting. Moreover,
-UCL compiled with optimizations (-O3) performs significantly faster:
-```
-ucl: parsed input in 0.3002 seconds
-ucl: emitted config in 0.1174 seconds
-ucl: emitted json in 0.1174 seconds
-ucl: emitted compact json in 0.0991 seconds
-ucl: emitted yaml in 0.1354 seconds
-```
-
-You can do your own benchmarks by running `make check` in libucl top directory.
-
-## Conclusion
-
-UCL has clear design that should be very convenient for reading and writing. At the same time it is compatible with
-JSON language and therefore can be used as a simple JSON parser. Macro logic provides an ability to extend configuration
-language (for example by including some lua code) and comments allow to disable or enable the parts of a configuration
-quickly.
+++ /dev/null
-# Lupa
-
-## Introduction
-
-Lupa is a [Jinja2][] template engine implementation written in Lua and supports
-Lua syntax within tags and variables.
-
-Lupa was sponsored by the [Library of the University of Antwerp][].
-
-[Jinja2]: http://jinja.pocoo.org
-[Library of the University of Antwerp]: http://www.uantwerpen.be/
-
-## Requirements
-
-Lupa has the following requirements:
-
-* [Lua][] 5.1, 5.2, or 5.3.
-* The [LPeg][] library.
-
-[Lua]: http://www.lua.org
-[LPeg]: http://www.inf.puc-rio.br/~roberto/lpeg/
-
-## Download
-
-Download Lupa from the project’s [download page][].
-
-[download page]: download
-
-## Installation
-
-Unzip Lupa and place the "lupa.lua" file in your Lua installation's
-`package.path`. This location depends on your version of Lua. Typical locations
-are listed below.
-
-* Lua 5.1: */usr/local/share/lua/5.1/* or */usr/local/share/lua/5.1/*
-* Lua 5.2: */usr/local/share/lua/5.2/* or */usr/local/share/lua/5.2/*
-* Lua 5.3: */usr/local/share/lua/5.3/* or */usr/local/share/lua/5.3/*
-
-You can also place the "lupa.lua" file wherever you'd like and add it to Lua's
-`package.path` manually in your program. For example, if Lupa was placed in a
-*/home/user/lua/* directory, it can be used as follows:
-
- package.path = package.path..';/home/user/lua/?.lua'
-
-## Usage
-
-Lupa is simply a Lua library. Its `lupa.expand()` and `lupa.expand_file()`
-functions may called to process templates. For example:
-
- lupa = require('lupa')
- lupa.expand("hello {{ s }}!", {s = "world"}) --> "hello world!"
- lupa.expand("{% for i in {1, 2, 3} %}{{ i }}{% endfor %}") --> 123
-
-By default, Lupa loads templates relative to the current working directory. This
-can be changed by reconfiguring Lupa:
-
- lupa.expand_file('name') --> expands template "./name"
- lupa.configure{loader = lupa.loaders.filesystem('path/to/templates')}
- lupa.expand_file('name') --> expands template "path/to/templates/name"
-
-See Lupa's [API documentation][] for more information.
-
-[API documentation]: api.html
-
-## Syntax
-
-Please refer to Jinja2's extensive [template documentation][]. Any
-incompatibilities are listed in the sections below.
-
-[template documentation]: http://jinja.pocoo.org/docs/dev/templates/
-
-## Comparison with Jinja2
-
-While Lua and Python (Jinja2's implementation language) share some similarities,
-the languages themselves are fundamentally different. Nevertheless, a
-significant effort was made to support a vast majority of Jinja2's Python-style
-syntax. As a result, Lupa passes Jinja2's test suite with only a handful of
-modifications. The comprehensive list of differences between Lupa and Jinja2 is
-described in the following sections.
-
-### Fundamental Differences
-
-* Expressions use Lua's syntax instead of Python's, so many of Python's
- syntactic constructs are not valid. However, the following constructs
- *are valid*, despite being invalid in pure Lua:
-
- + Iterating over table literals or table variables directly in a "for" loop:
-
- {% for i in {1, 2, 3} %}...{% endfor %}
-
- + Conditional loops via an "if" expression suffix:
-
- {% for x in range(10) if is_odd(x) %}...{% endfor %}
-
- + Table unpacking for list elements when iterating through a list of lists:
-
- {% for a, b, c in {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}} %}...{% endfor %}
-
- + Default values for macro arguments:
-
- {% macro m(a, b, c='c', d='d') %}...{% endmacro %}
-
-* Strings do not have unicode escapes nor is unicode interpreted in any way.
-
-### Syntactic Differences
-
-* Line statements are not supported due to parsing complexity.
-* In `{% for ... %}` loops, the `loop.length`, `loop.revindex`,
- `loop.revindex0`, and `loop.last` variables only apply to sequences, where
- Lua's `'#'` operator applies.
-* The `{% continue %}` and `{% break %}` loop controls are not supported due to
- complexity.
-* Loops may be used recursively by default, so the `recursive` loop modifier is
- not supported.
-* The `is` operator is not supported by Lua, so tests of the form `{{ x is y }}`
- should be written `{{ is_y(x) }}` (e.g. `{{ is_number(42) }}`).
-* Filters cannot occur after tokens within an expression (e.g.
- `{{ "foo"|upper .. "bar"|upper }}`), but can only occur at the end of an
- expression (e.g. `{{ "foo".."bar"|upper }}`).
-* Blocks always have access to scoped variables, so the `scoped` block modifier
- is not supported.
-* Named block end tags are not supported since the parser cannot easily keep
- track of that state information.
-* Any `{% block ... %}` tags within a "false" block (e.g. `{% if a %}` where `a`
- evaluates to `false`) are never read and stored due to the parser
- implementation.
-* Inline "if" expressions (e.g. `{% extends b if a else c %}`) are not
- supported. Instead, use a Lua conditional expression
- (e.g. `{% extends a and b or c %}`).
-* Any `{% extends ... %}` tags within a sub-scope are not effective outside that
- scope (e.g. `{% if a %}{% extends a %}{% else %}{% extends b %}{% endif %}`).
- Instead, use a Lua conditional expression (e.g. `{% extends a or b %}`).
-* Macros are simply Lua functions and have no metadata attributes.
-* Macros do not have access to a `kwargs` variable since Lua does not support
- keyword arguments.
-* `{% from x import y %}` tags are not supported. Instead, you must use either
- `{% import x %}`, which imports all globals in `x` into the current
- environment, or use `{% import x as z %}`, which imports all globals in `x`
- into the variable `z`.
-* `{% set ... %}` does not support multiple assignment. Use `{% do ...%}`
- instead. The catch is that `{% do ... %}` does not support filters.
-* The `{% trans %}` and `{% endtrans %}` tags, `{% with %}` and `{% endwith %}`
- tags, and `{% autoescape %}` and `{% endautoescape %}` tags are not supported
- since they are outside the scope of this implementation.
-
-### Filter Differences
-
-* Only the `batch`, `groupby`, and `slice` filters return generators which
- produce one item at a time when looping. All other filters that produce
- iterable results generate all items at once.
-* The `float` filter only works in Lua 5.3 since that version of Lua has a
- distinction between floats and integers.
-* The `safe` filter must appear at the end of a filter chain since its output
- cannot be passed to any other filter.
-
-### Function Differences
-
-* The global `range(n)` function returns a sequence from 1 to `n`, inclusive,
- since lists start at 1 in Lua.
-* No `lipsum()`, `dict()`, or `joiner()` functions for the sake of simplicity.
-
-### API Differences
-
-* Lupa has a much simpler API consisting of just four functions and three
- fields:
-
- + `lupa.expand()`: Expands a string template subject to an environment.
- + `lupa.expand_file()`: Expands a file template subject to an environment.
- + `lupa.configure()` Configures delimiters and template options.
- + `lupa.reset()`: Resets delimiters and options to their defaults.
- + `lupa.env`: The default environment for templates.
- + `lupa.filters`: The set of available filters (`escape`, `join`, etc.).
- + `lupa.tests`: The set of available tests (`is_odd`, `is_defined`, etc.).
-
-* There is no bytecode caching.
-* Lupa has no extension mechanism. Instead, modify `lupa.env`, `lupa.filters`,
- and `lupa.tests` directly. However, the parser cannot be extended.
-* Sandboxing is not supported, although `lupa.env` is safe by default (`io`,
- `os.execute`, `os.remove`, etc. are not available).
+++ /dev/null
-# Public suffixes list
-
-Update procedure:
-
-1. Download the list from the [official mirror](https://publicsuffix.org/list/public_suffix_list.dat)
-2. Proceed through `idn.pl` script
-
-1 liner: `curl https://publicsuffix.org/list/public_suffix_list.dat | perl idn.pl > effective_tld_names.dat`
-
-## Deps installation
-
-Ensure that you have `cpanm` installed (e.g. by `brew install cpanm`).
-Run `cpanm --installdeps .` once.
+++ /dev/null
-# Read Evaluate Print Loop ++
-
-
-
-[](https://travis-ci.org/AmokHuginnsson/replxx)
-
-A small, portable GNU readline replacement for Linux, Windows and
-MacOS which is capable of handling UTF-8 characters. Unlike GNU
-readline, which is GPL, this library uses a BSD license and can be
-used in any kind of program.
-
-## Origin
-
-This replxx implementation is based on the work by
-[ArangoDB Team](https://github.com/arangodb/linenoise-ng) and
-[Salvatore Sanfilippo](https://github.com/antirez/linenoise) and
-10gen Inc. The goal is to create a zero-config, BSD
-licensed, readline replacement usable in Apache2 or BSD licensed
-programs.
-
-## Features
-
-* single-line and multi-line editing mode with the usual key bindings implemented
-* history handling
-* completion
-* syntax highlighting
-* hints
-* BSD license source code
-* Only uses a subset of VT100 escapes (ANSI.SYS compatible)
-* UTF8 aware
-* support for Linux, MacOS and Windows
-
-It deviates from Salvatore's original goal to have a minimal readline
-replacement for the sake of supporting UTF8 and Windows. It deviates
-from 10gen Inc.'s goal to create a C++ interface to linenoise. This
-library uses C++ internally, but to the user it provides a pure C
-interface that is compatible with the original linenoise API.
-C interface.
-
-## Requirements
-
-To build this library, you will need a C++11-enabled compiler and
-some recent version of CMake.
-
-## Build instructions
-
-### *nix
-
-1. Create a build directory
-
-```bash
-mkdir -p build && cd build
-```
-
-2. Build the library
-
-```bash
-cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release .. && make
-```
-
-3. Install the library at the default target location
-
-```bash
-sudo make install
-```
-
-The default installation location can be adjusted by setting the `DESTDIR`
-variable when invoking `make install`:
-
-```bash
-make DESTDIR=/tmp install
-```
-
-### Windows
-
-1. Create a build directory in MS-DOS command prompt
-
-```
-md build
-cd build
-```
-
-2. Generate Visual Studio solution file with cmake
-
-* 32 bit:
-```bash
-cmake -G "Visual Studio 12 2013" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ..`
-```
-* 64 bit:
-```bash
-`cmake -G "Visual Studio 12 2013 Win64" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ..`
-```
-
-3. Open the generated file `replxx.sln` in the `build` subdirectory with Visual Studio.
-
-## Tested with...
-
- * Linux text only console ($TERM = linux)
- * Linux KDE terminal application ($TERM = xterm)
- * Linux xterm ($TERM = xterm)
- * Linux Buildroot ($TERM = vt100)
- * Mac OS X iTerm ($TERM = xterm)
- * Mac OS X default Terminal.app ($TERM = xterm)
- * OpenBSD 4.5 through an OSX Terminal.app ($TERM = screen)
- * IBM AIX 6.1
- * FreeBSD xterm ($TERM = xterm)
- * ANSI.SYS
- * Emacs comint mode ($TERM = dumb)
- * Windows
-
-Please test it everywhere you can and report back!
-
-## Let's push this forward!
-
-Patches should be provided in the respect of linenoise sensibility for
-small and easy to understand code that and the license
-restrictions. Extensions must be submitted under a BSD license-style.
-A contributor license is required for contributions.
-
+++ /dev/null
-Authors
-=======
-
-Martin Porter
--------------
-
- - Designed the snowball language.
- - Implemented the snowball to C compiler.
- - Implemented the stemming algorithms in C.
- - Wrote the documentation.
-
-Richard Boulton
----------------
-
- - Implemented Java backend of the snowball compiler.
- - Developed build system.
- - Assisted with website maintenance.
-
-
-Assistance from
----------------
-
-Olivier Bornet - fixes to java packaging and build system.
-Andreas Jung - useful bug reports on the libstemmer library.
-Olly Betts - several patches, bug reports, and performance improvements.
-Sebastiano Vigna and Oerd Cukalla - patches for the Java stemming algorithms.
-Ralf Junker - fix a potential memory leak in sb_stemmer_new().
+++ /dev/null
-Snowball 2.0.0 (2019-10-02)
-===========================
-
-C/C++
------
-
-* Fully handle 4-byte UTF-8 sequences. Previously `hop` and `next` handled
- sequences of any length, but commands which look at the character value only
- handled sequences up to length 3. Fixes #89.
-
-* Fix handling of a 3-byte UTF-8 sequence in a grouping in `backwardmode`.
-
-Java
-----
-
-* TestApp.java:
-
- - Always use UTF-8 for I/O. Patch from David Corbett (#80).
-
- - Allow reading input from stdin.
-
- - Remove rather pointless "stem n times" feature.
-
- - Only lower case ASCII to match stemwords.c.
-
- - Stem empty lines too to match stemwords.c.
-
-Code Quality Improvements
--------------------------
-
-* Fix various warnings from newer compilers.
-
-* Improve use of `const`.
-
-* Share common functions between compiler backends rather than having multiple
- copies of the same code.
-
-* Assorted code clean-up.
-
-* Initialise line_labelled member of struct generator to 0. Previously we were
- invoking undefined behaviour, though in practice it'll be zero initialised on
- most platforms.
-
-New Code Generators
--------------------
-
-* Add Python generator (#24). Originally written by Yoshiki Shibukawa, with
- additional updates by Dmitry Shachnev.
-
-* Add Javascript generator. Based on JSX generator (#26) written by Yoshiki
- Shibukawa.
-
-* Add Rust generator from Jakob Demler (#51).
-
-* Add Go generator from Marty Schoch (#57).
-
-* Add C# generator. Based on patch from Cesar Souza (#16, #17).
-
-* Add Pascal generator. Based on Delphi backend from stemming.zip file on old
- website (#75).
-
-New Language Features
----------------------
-
-* Add `len` and `lenof` to measure Unicode length. These are similar to `size`
- and `sizeof` (respectively), but `size` and `sizeof` return the length in
- bytes under `-utf8`, whereas these new commands give the same result whether
- using `-utf8`, `-widechars` or neither (but under `-utf8` they are O(n) in
- the length of the string). For compatibility with existing code which might
- use these as variable or function names, they stop being treated as tokens if
- declared to be a variable or function.
-
-* New `{U+1234}` stringdef notation for Unicode codepoints.
-
-* More versatile integer tests. Now you can compare any two arithmetic
- expressions with a relational operator in parentheses after the `$`, so for
- example `$(len > 3)` can now be used when previously a temporary variable was
- required: `$tmp = len $tmp > 3`
-
-Code generation improvements
-----------------------------
-
-* General:
-
- + Avoid unnecessarily saving and restoring of the cursor for more commands -
- `atlimit`, `do`, `set` and `unset` all leave the cursor alone or always
- restore its value, and for C `booltest` (which other languages already
- handled).
-
- + Special case handling for `setlimit tomark AE`. All uses of setlimit in
- the current stemmers we ship follow this pattern, and by special-casing we
- can avoid having to save and restore the cursor (#74).
-
- + Merge duplicate actions in the same `among`. This reduces the size of the
- switch/if-chain in the generated code which dispatch the among for many of
- the stemmers.
-
- + Generate simpler code for `among`. We always check for a zero return value
- when we call the among, so there's no point also checking for that in the
- switch/if-chain. We can also avoid the switch/if-chain entirely when
- there's only one possible outcome (besides the zero return).
-
- + Optimise code generated for `do <function call>`. This speeds up "make
- check_python" by about 2%, and should speed up other interpreted languages
- too (#110).
-
- + Generate more and better comments referencing snowball source.
-
- + Add homepage URL and compiler version as comments in generated files.
-
-* C/C++:
-
- + Fix `size` and `sizeof` to not report one too high (reported by Assem
- Chelli in #32).
-
- + If signal `f` from a function call would lead to return from the current
- function then handle this and bailing out on an error together with a
- simple `if (ret <= 0) return ret;`
-
- + Inline testing for a single character literals.
-
- + Avoiding generating `|| 0` in corner case - this can result in a compiler
- warning when building the generated code.
-
- + Implement `insert_v()` in terms of `insert_s()`.
-
- + Add conditional `extern "C"` so `runtime/api.h` can be included from C++
- code. Closes #90, reported by vvarma.
-
-* Java:
-
- + Fix functions in `among` to work in Java. We seem to need to make the
- methods called from among `public` instead of `private`, and to call them
- on `this` instead of the `methodObject` (which is cleaner anyway). No
- revision in version control seems to generate working code for this case,
- but Richard says it definitely used to work - possibly older JVMs failed to
- correctly enforce the access controls when methods were invoked by
- reflection.
-
- + Code after handling `f` by returning from the current function is
- unreachable too.
-
- + Previously we incorrectly decided that code after an `or` was
- unreachable in certain cases. None of the current stemmers in the
- distribution triggered this, but Martin Porter's snowball version
- of the Schinke Latin stemmer does. Fixes #58, reported by Alexander
- Myltsev.
-
- + The reachability logic was failing to consider reachability from
- the final command in an `or`. Fixes #82, reported by David Corbett.
-
- + Fix `maxint` and `minint`. Patch from David Corbett in #31.
-
- + Fix `$` on strings. The previous generated code was just wrong. This
- doesn't affect any of the included algorithms, but for example breaks
- Martin Porter's snowball implementation of Schinke's Latin Stemmer.
- Issue noted by Jakob Demler while working on the Rust backend in #51,
- and reported in the Schinke's Latin Stemmer by Alexander Myltsev
- in #58.
-
- + Make SnowballProgram objects serializable. Patch from Oleg Smirnov in #43.
-
- + Eliminate range-check implementation for groupings. This was removed from
- the C generator 10 years earlier, isn't used for any of the existing
- algorithms, and it doesn't seem likely it would be - the grouping would
- have to consist entirely of a contiguous block of Unicode code-points.
-
- + Simplify code generated for `repeat` and `atleast`.
-
- + Eliminate unused return values and variables from runtime functions.
-
- + Only import the `among` and `SnowballProgram` classes if they're actually
- used.
-
- + Only generate `copy_from()` method if it's used.
-
- + Merge runtime functions `eq_s` and `eq_v` functions.
-
- + Java arrays know their own length so stop storing it separately.
-
- + Escape char 127 (DEL) in generated Java code. It's unlikely that this
- character would actually be used in a real stemmer, so this was more of a
- theoretical bug.
-
- + Drop unused import of InvocationTargetException from SnowballStemmer.
- Reported by GerritDeMeulder in #72.
-
- + Fix lint check issues in generated Java code. The stemmer classes are only
- referenced in the example app via reflection, so add
- @SuppressWarnings("unused") for them. The stemmer classes override
- equals() and hashCode() methods from the standard java Object class, so
- mark these with @Override. Both suggested by GerritDeMeulder in #72.
-
- + Declare Java variables at point of use in generated code. Putting all
- declarations at the top of the function was adding unnecessary complexity
- to the Java generator code for no benefit.
-
- + Improve formatting of generated code.
-
-New stemming algorithms
------------------------
-
-* Add Tamil stemmer from Damodharan Rajalingam (#2, #3).
-
-* Add Arabic stemmer from Assem Chelli (#32, #50).
-
-* Add Irish stemmer Jim O'Regan (#48).
-
-* Add Nepali stemmer from Arthur Zakirov (#70).
-
-* Add Indonesian stemmer from Olly Betts (#71).
-
-* Add Hindi stemmer from Olly Betts (#73). Thanks to David Corbett for review.
-
-* Add Lithuanian stemmer from Dainius Jocas (#22, #76).
-
-* Add Greek stemmer from Oleg Smirnov (#44).
-
-* Add Catalan and Basque stemmers from Israel Olalla (#104).
-
-Behavioural changes to existing algorithms
-------------------------------------------
-
-* Portuguese:
-
- + Replace incorrect Spanish suffixes by Portuguese suffixes (#1).
-
-* French:
-
- + The MSDOS CP850 version of the French algorithm was missing changes present
- in the ISO8859-1 and Unicode versions. There's now a single version of
- each algorithm which was based on the Unicode version.
-
- + Recognize French suffixes even when they begin with diaereses. Patch from
- David Corbett in #78.
-
-* Russian:
-
- + We now normalise 'ё' to 'е' before stemming. The documentation has long
- said "we assume ['ё'] is mapped into ['е']" but it's more convenient for
- the stemmer to actually perform this normalisation. This change has no
- effect if the caller is already normalising as we recommend. It's a change
- in behaviour they aren't, but 'ё' occurs rarely (there are currently no
- instances in our test vocabulary) and this improves behaviour when it does
- occur. Patch from Eugene Mirotin (#65, #68).
-
-* Finish:
-
- + Adjust the Finnish algorithm not to mangle numbers. This change also
- means it tends to leave foreign words alone. Fixes #66.
-
-* Danish:
-
- + Adjust Danish algorithm not to mangle alphanumeric codes. In particular
- alphanumeric codes ending in a double digit (e.g. 0x0e00, hal9000,
- space1999) are no longer mangled. See #81.
-
-Optimisations to existing algorithms
-------------------------------------
-
-* Turkish:
-
- + Simplify uses of `test` in stemmer code.
-
- + Check for 'ad' or 'soyad' more efficiently, and without needing the
- strlen variable. This speeds up "make check_utf8_turkish" by 11%
- on x86 Linux.
-
-* Kraaij-Pohlmann:
-
- + Eliminate variable x `$p1 <= cursor` is simpler and a little more efficient
- than `setmark x $x >= p1`.
-
-Code clarity improvements to existing algorithms
-------------------------------------------------
-
-* Turkish:
-
- + Use , for cedilla to match the conventions used in other stemmers.
-
-* Kraaij-Pohlmann:
-
- + Avoid cryptic `[among ( (])` ... `)` construct - instead use the same
- `[substring] among (` ... `)` construct we do in other stemmers.
-
-Compiler
---------
-
-* Support conventional --help and --version options.
-
-* Warn if -r or -ep used with backend other than C/C++.
-
-* Warn if encoding command line options are specified when generating code in a
- language with a fixed encoding.
-
-* The default classname is now set based on the output filename, so `-n` is now
- often no longer needed. Fixes #64.
-
-* Avoid potential one byte buffer over-read when parsing snowball code.
-
-* Avoid comparing with uninitialised array element during compilation.
-
-* Improve `-syntax` output for `setlimit L for C`.
-
-* Optimise away double negation so generators don't have to worry about
- generating `--` (decrement operator in many languages). Fixes #52, reported
- by David Corbett.
-
-* Improved compiler error and warning messages:
-
- - We now report FILE:LINE: before each diagnostic message.
-
- - Improve warnings for unused declarations/definitions.
-
- - Warn for variables which are used, but either never initialised
- or never read.
-
- - Flag non-ASCII literal strings. This is an error for wide Unicode, but
- only a warning for single-byte and UTF-8 which work so long as the source
- encoding matches the encoding used in the generated stemmer code.
-
- - Improve error recovery after an undeclared `define`. We now sniff the
- token after the identifier and if it is `as` we parse as a routine,
- otherwise we parse as a grouping. Previously we always just assumed it was
- a routine, which gave a confusing second error if it was a grouping.
-
- - Improve error recovery after an unexpected token in `among`. Previously
- we acted as if the unexpected token closed the `among` (this probably
- wasn't intended but just a missing `break;` in a switch statement). Now we
- issue an error and try the next token.
-
-* Report error instead of silently truncating character values (e.g. `hex 123`
- previously silently became byte 0x23 which is `#` rather than a
- g-with-cedilla).
-
-* Enlarge the initial input buffer size to 8192 bytes and double each time we
- hit the end. Snowball programs are typically a few KB in size (with the
- current largest we ship being the Greek stemmer at 27KB) so the previous
- approach of starting with a 10 byte input buffer and increasing its size by
- 50% plus 40 bytes each time it filled was inefficient, needing up to 15
- reallocations to load greek.sbl.
-
-* Identify variables only used by one `routine`/`external`. This information
- isn't yet used, but such variables which are also always written to before
- being read can be emitted as local variables in most target languages.
-
-* We now allow multiple source files on command line, and allow them to be
- after (or even interspersed) with options to better match modern Unix
- conventions. Support for multiple source files allows specifying a single
- byte character set mapping via a source file of `stringdef`.
-
-* Avoid infinite recursion in compiler when optimising a recursive snowball
- function. Recursive functions aren't typical in snowball programs, but
- the compiler shouldn't crash for any input, especially not a valid one.
- We now simply limit on how deep the compiler will recurse and make the
- pessimistic assumption in the unlikely event we hit this limit.
-
-Build system:
-
-* `make clean` in C libstemmer_c distribution now removes `examples/*.o`.
- (#59)
-
-* Fix all the places which previously had to have a list of stemmers to work
- dynamically or be generated, so now only modules.txt needs updating to add
- a new stemmer.
-
-* Add check_java make target which runs tests for java.
-
-* Support gzipped test data (the uncompressed arabic test data is too big for
- github).
-
-* GNUmakefile: Drop useless `-eprefix` and `-r` options from snowball
- invocations for Java - these are only meaningful when generating C code.
-
-* Pass CFLAGS when linking which matches convention (e.g. automake does it) and
- facilitates use of tools such as ASan. Fixes #84, reported by Thomas
- Pointhuber.
-
-* Add CI builds with -std=c90 to check compiler and generated code are C90
- (#54)
-
-libstemmer stuff:
-
-* Split out CPPFLAGS from CFLAGS and use CFLAGS when linking stemwords.
-
-* Add -O2 to CFLAGS.
-
-* Make generated tables of encodings and modules const.
-
-* Fix clang static analyzer memory leak warning (in practice this code path
- can never actually be taken). Patch from Patrick O. Perry (#56)
-
-documentation
-
-* Added copyright and licensing details (#10).
-
-* Document that libstemmer supports ISO_8859_2 encoding. Currently hungarian
- and romanian are available in ISO_8859_2.
-
-* Remove documentation falsely claiming that libstemmer supports CP850
- encoding.
-
-* CONTRIBUTING.rst: Add guidance for contributing new stemming algorithms and
- new language backends.
-
-* Overhaul libstemmer_python_README. Most notably, replace the benchmark data
- which was very out of date.
+++ /dev/null
-This contains the source code for the snowball compiler and the stemming
-algorithms on the website.
-
-See http://snowball.tartarus.org/ for more details.
-
+++ /dev/null
-Things to do:
-
- - Write documentation for how to use libstemmer (as opposed to how stemming
- algorithms themselves work).
- Currently, the documentation in the include/libstemmer.h header file is
- pretty clear and comprehensive, but an overview document wouldn't go amiss.
-
-Things that would be nice to include at some point.
-
- - Add version numbers to each stemming algorithm, and allow the interface to
- request a specific version of the stemming algorithms. Default to providing
- the latest version of the algorithm.
- - Make mkmodules.pl generate the build system, instead of being called from it.
- This would allow it to generate the list of modules to be built, so that it's
- not necessary to change things in more than one place to add a new algorithm.
+++ /dev/null
-libstemmer_c
-============
-
-This document pertains to the C version of the libstemmer distribution,
-available for download from:
-
-http://snowball.tartarus.org/dist/libstemmer_c.tgz
-
-
-Compiling the library
-=====================
-
-A simple makefile is provided for Unix style systems. On such systems, it
-should be possible simply to run "make", and the file "libstemmer.o"
-and the example program "stemwords" will be generated.
-
-If this doesn't work on your system, you need to write your own build
-system (or call the compiler directly). The files to compile are
-all contained in the "libstemmer", "runtime" and "src_c" directories,
-and the public header file is contained in the "include" directory.
-
-The library comes in two flavours; UTF-8 only, and UTF-8 plus other character
-sets. To use the utf-8 only flavour, compile "libstemmer_utf8.c" instead of
-"libstemmer.c".
-
-For convenience "mkinc.mak" is a makefile fragment listing the source files and
-header files used to compile the standard version of the library.
-"mkinc_utf8.mak" is a comparable makefile fragment listing just the source
-files for the UTF-8 only version of the library.
-
-
-Using the library
-=================
-
-The library provides a simple C API. Essentially, a new stemmer can
-be obtained by using "sb_stemmer_new". "sb_stemmer_stem" is then
-used to stem a word, "sb_stemmer_length" returns the stemmed
-length of the last word processed, and "sb_stemmer_delete" is
-used to delete a stemmer.
-
-Creating a stemmer is a relatively expensive operation - the expected
-usage pattern is that a new stemmer is created when needed, used
-to stem many words, and deleted after some time.
-
-Stemmers are re-entrant, but not threadsafe. In other words, if
-you wish to access the same stemmer object from multiple threads,
-you must ensure that all access is protected by a mutex or similar
-device.
-
-libstemmer does not currently incorporate any mechanism for caching the results
-of stemming operations. Such caching can greatly increase the performance of a
-stemmer under certain situations, so suitable patches will be considered for
-inclusion.
-
-The standard libstemmer sources contain an algorithm for each of the supported
-languages. The algorithm may be selected using the english name of the
-language, or using the 2 or 3 letter ISO 639 language codes. In addition,
-the traditional "Porter" stemming algorithm for english is included for
-backwards compatibility purposes, but we recommend use of the "English"
-stemmer in preference for new projects.
-
-(Some minor algorithms which are included only as curiosities in the snowball
-website, such as the Lovins stemmer and the Kraaij Pohlmann stemmer, are not
-included in the standard libstemmer sources. These are not really supported by
-the snowball project, but it would be possible to compile a modified libstemmer
-library containing these if desired.)
-
-
-The stemwords example
-=====================
-
-The stemwords example program allows you to run any of the stemmers
-compiled into the libstemmer library on a sample vocabulary. For
-details on how to use it, run it with the "-h" command line option.
-
-
-Using the library in a larger system
-====================================
-
-If you are incorporating the library into the build system of a larger
-program, I recommend copying the unpacked tarball without modification into
-a subdirectory of the sources of your program. Future versions of the
-library are intended to keep the same structure, so this will keep the
-work required to move to a new version of the library to a minimum.
-
-As an additional convenience, the list of source and header files used
-in the library is detailed in mkinc.mak - a file which is in a suitable
-format for inclusion by a Makefile. By including this file in your build
-system, you can link the snowball system into your program with a few
-extra rules.
-
-Using the library in a system using GNU autotools
-=================================================
-
-The libstemmer_c library can be integrated into a larger system which uses the
-GNU autotool framework (and in particular, automake and autoconf) as follows:
-
-1) Unpack libstemmer_c.tgz in the top level project directory so that there is
- a libstemmer_c subdirectory of the top level directory of the project.
-
-2) Add a file "Makefile.am" to the unpacked libstemmer_c folder, containing:
-
-noinst_LTLIBRARIES = libstemmer.la
-include $(srcdir)/mkinc.mak
-noinst_HEADERS = $(snowball_headers)
-libstemmer_la_SOURCES = $(snowball_sources)
-
-(You may also need to add other lines to this, for example, if you are using
-compiler options which are not compatible with compiling the libstemmer
-library.)
-
-3) Add libstemmer_c to the AC_CONFIG_FILES declaration in the project's
- configure.ac file.
-
-4) Add to the top level makefile the following lines (or modify existing
- assignments to these variables appropriately):
-
-AUTOMAKE_OPTIONS = subdir-objects
-AM_CPPFLAGS = -I$(top_srcdir)/libstemmer_c/include
-SUBDIRS=libstemmer_c
-<name>_LIBADD = libstemmer_c/libstemmer.la
-
-(Where <name> is the name of the library or executable which links against
-libstemmer.)
-
+++ /dev/null
-libstemmer_java
-===============
-
-This document pertains to the Java version of the libstemmer distribution,
-available for download from:
-
-http://snowball.tartarus.org/dist/libstemmer_java.tgz
-
-
-Compiling the library
-=====================
-
-Simply run the java compiler on all the java source files under the java
-directory. For example, this can be done under unix by changing directory into
-the java directory, and running:
-
- javac org/tartarus/snowball/*.java org/tartarus/snowball/ext/*.java
-
-This will compile the library and also an example program "TestApp" which
-provides a command line interface to the library.
-
-
-Using the library
-=================
-
-There is currently no formal documentation on the use of the Java version
-of the library. Additionally, its interface is not guaranteed to be
-stable.
-
-The best documentation of the library is the source of the TestApp example
-program.
-
-
-The TestApp example
-===================
-
-The TestApp example program allows you to run any of the stemmers
-compiled into the libstemmer library on a sample vocabulary. For
-details on how to use it, run it with no command line parameters.
-
+++ /dev/null
-v1.4.5
-fix : Compression ratio regression on huge files (> 3 GB) using high levels (--ultra) and multithreading, by @terrelln
-perf: Improved decompression speed: x64 : +10% (clang) / +5% (gcc); ARM : from +15% to +50%, depending on SoC, by @terrelln
-perf: Automatically downsizes ZSTD_DCtx when too large for too long (#2069, by @bimbashreshta)
-perf: Improved fast compression speed on aarch64 (#2040, ~+3%, by @caoyzh)
-perf: Small level 1 compression speed gains (depending on compiler)
-cli : New --patch-from command, create and apply patches from files, by @bimbashreshta
-cli : New --filelist= : Provide a list of files to operate upon from a file
-cli : -b -d command can now benchmark decompression on multiple files
-cli : New --no-content-size command
-cli : New --show-default-cparams information command
-api : ZDICT_finalizeDictionary() is promoted to stable (#2111)
-api : new experimental parameter ZSTD_d_stableOutBuffer (#2094)
-build: Generate a single-file libzstd library (#2065, by @cwoffenden)
-build: Relative includes no longer require -I compiler flags for zstd lib subdirs (#2103, by @felixhandte)
-build: zstd now compiles cleanly under -pedantic (#2099)
-build: zstd now compiles with make-4.3
-build: Support mingw cross-compilation from Linux, by @Ericson2314
-build: Meson multi-thread build fix on windows
-build: Some misc icc fixes backed by new ci test on travis
-misc: bitflip analyzer tool, by @felixhandte
-misc: Extend largeNbDicts benchmark to compression
-misc: Edit-distance match finder in contrib/
-doc : Improved beginner CONTRIBUTING.md docs
-doc : New issue templates for zstd
-
-v1.4.4
-perf: Improved decompression speed, by > 10%, by @terrelln
-perf: Better compression speed when re-using a context, by @felixhandte
-perf: Fix compression ratio when compressing large files with small dictionary, by @senhuang42
-perf: zstd reference encoder can generate RLE blocks, by @bimbashrestha
-perf: minor generic speed optimization, by @davidbolvansky
-api: new ability to extract sequences from the parser for analysis, by @bimbashrestha
-api: fixed decoding of magic-less frames, by @terrelln
-api: fixed ZSTD_initCStream_advanced() performance with fast modes, reported by @QrczakMK
-cli: Named pipes support, by @bimbashrestha
-cli: short tar's extension support, by @stokito
-cli: command --output-dir-flat= , generates target files into requested directory, by @senhuang42
-cli: commands --stream-size=# and --size-hint=#, by @nmagerko
-cli: command --exclude-compressed, by @shashank0791
-cli: faster `-t` test mode
-cli: improved some error messages, by @vangyzen
-cli: fix command `-D dictionary` on Windows, reported by @artyompetrov
-cli: fix rare deadlock condition within dictionary builder, by @terrelln
-build: single-file decoder with emscripten compilation script, by @cwoffenden
-build: fixed zlibWrapper compilation on Visual Studio, reported by @bluenlive
-build: fixed deprecation warning for certain gcc version, reported by @jasonma163
-build: fix compilation on old gcc versions, by @cemeyer
-build: improved installation directories for cmake script, by Dmitri Shubin
-pack: modified pkgconfig, for better integration into openwrt, requested by @neheb
-misc: Improved documentation : ZSTD_CLEVEL, DYNAMIC_BMI2, ZSTD_CDict, function deprecation, zstd format
-misc: fixed educational decoder : accept larger literals section, and removed UNALIGNED() macro
-
-v1.4.3
-bug: Fix Dictionary Compression Ratio Regression by @cyan4973 (#1709)
-bug: Fix Buffer Overflow in legacy v0.3 decompression by @felixhandte (#1722)
-build: Add support for IAR C/C++ Compiler for Arm by @joseph0918 (#1705)
-
-v1.4.2
-bug: Fix bug in zstd-0.5 decoder by @terrelln (#1696)
-bug: Fix seekable decompression in-memory API by @iburinoc (#1695)
-misc: Validate blocks are smaller than size limit by @vivekmg (#1685)
-misc: Restructure source files by @ephiepark (#1679)
-
-v1.4.1
-bug: Fix data corruption in niche use cases by @terrelln (#1659)
-bug: Fuzz legacy modes, fix uncovered bugs by @terrelln (#1593, #1594, #1595)
-bug: Fix out of bounds read by @terrelln (#1590)
-perf: Improve decode speed by ~7% @mgrice (#1668)
-perf: Slightly improved compression ratio of level 3 and 4 (ZSTD_dfast) by @cyan4973 (#1681)
-perf: Slightly faster compression speed when re-using a context by @cyan4973 (#1658)
-perf: Improve compression ratio for small windowLog by @cyan4973 (#1624)
-perf: Faster compression speed in high compression mode for repetitive data by @terrelln (#1635)
-api: Add parameter to generate smaller dictionaries by @tyler-tran (#1656)
-cli: Recognize symlinks when built in C99 mode by @felixhandte (#1640)
-cli: Expose cpu load indicator for each file on -vv mode by @ephiepark (#1631)
-cli: Restrict read permissions on destination files by @chungy (#1644)
-cli: zstdgrep: handle -f flag by @felixhandte (#1618)
-cli: zstdcat: follow symlinks by @vejnar (#1604)
-doc: Remove extra size limit on compressed blocks by @felixhandte (#1689)
-doc: Fix typo by @yk-tanigawa (#1633)
-doc: Improve documentation on streaming buffer sizes by @cyan4973 (#1629)
-build: CMake: support building with LZ4 @leeyoung624 (#1626)
-build: CMake: install zstdless and zstdgrep by @leeyoung624 (#1647)
-build: CMake: respect existing uninstall target by @j301scott (#1619)
-build: Make: skip multithread tests when built without support by @michaelforney (#1620)
-build: Make: Fix examples/ test target by @sjnam (#1603)
-build: Meson: rename options out of deprecated namespace by @lzutao (#1665)
-build: Meson: fix build by @lzutao (#1602)
-build: Visual Studio: don't export symbols in static lib by @scharan (#1650)
-build: Visual Studio: fix linking by @absotively (#1639)
-build: Fix MinGW-W64 build by @myzhang1029 (#1600)
-misc: Expand decodecorpus coverage by @ephiepark (#1664)
-
-v1.4.0
-perf: Improve level 1 compression speed in most scenarios by 6% by @gbtucker and @terrelln
-api: Move the advanced API, including all functions in the staging section, to the stable section
-api: Make ZSTD_e_flush and ZSTD_e_end block for maximum forward progress
-api: Rename ZSTD_CCtxParam_getParameter to ZSTD_CCtxParams_getParameter
-api: Rename ZSTD_CCtxParam_setParameter to ZSTD_CCtxParams_setParameter
-api: Don't export ZSTDMT functions from the shared library by default
-api: Require ZSTD_MULTITHREAD to be defined to use ZSTDMT
-api: Add ZSTD_decompressBound() to provide an upper bound on decompressed size by @shakeelrao
-api: Fix ZSTD_decompressDCtx() corner cases with a dictionary
-api: Move ZSTD_getDictID_*() functions to the stable section
-api: Add ZSTD_c_literalCompressionMode flag to enable or disable literal compression by @terrelln
-api: Allow compression parameters to be set when a dictionary is used
-api: Allow setting parameters before or after ZSTD_CCtx_loadDictionary() is called
-api: Fix ZSTD_estimateCStreamSize_usingCCtxParams()
-api: Setting ZSTD_d_maxWindowLog to 0 means use the default
-cli: Ensure that a dictionary is not used to compress itself by @shakeelrao
-cli: Add --[no-]compress-literals flag to enable or disable literal compression
-doc: Update the examples to use the advanced API
-doc: Explain how to transition from old streaming functions to the advanced API in the header
-build: Improve the Windows release packages
-build: Improve CMake build by @hjmjohnson
-build: Build fixes for FreeBSD by @lwhsu
-build: Remove redundant warnings by @thatsafunnyname
-build: Fix tests on OpenBSD by @bket
-build: Extend fuzzer build system to work with the new clang engine
-build: CMake now creates the libzstd.so.1 symlink
-build: Improve Menson build by @lzutao
-misc: Fix symbolic link detection on FreeBSD
-misc: Use physical core count for -T0 on FreeBSD by @cemeyer
-misc: Fix zstd --list on truncated files by @kostmo
-misc: Improve logging in debug mode by @felixhandte
-misc: Add CirrusCI tests by @lwhsu
-misc: Optimize dictionary memory usage in corner cases
-misc: Improve the dictionary builder on small or homogeneous data
-misc: Fix spelling across the repo by @jsoref
-
-v1.3.8
-perf: better decompression speed on large files (+7%) and cold dictionaries (+15%)
-perf: slightly better compression ratio at high compression modes
-api : finalized advanced API, last stage before "stable" status
-api : new --rsyncable mode, by @terrelln
-api : support decompression of empty frames into NULL (used to be an error) (#1385)
-build: new set of macros to build a minimal size decoder, by @felixhandte
-build: fix compilation on MIPS32, reported by @clbr (#1441)
-build: fix compilation with multiple -arch flags, by @ryandesign
-build: highly upgraded meson build, by @lzutao
-build: improved buck support, by @obelisk
-build: fix cmake script : can create debug build, by @pitrou
-build: Makefile : grep works on both colored consoles and systems without color support
-build: fixed zstd-pgo, by @bmwiedemann
-cli : support ZSTD_CLEVEL environment variable, by @yijinfb (#1423)
-cli : --no-progress flag, preserving final summary (#1371), by @terrelln
-cli : ensure destination file is not source file (#1422)
-cli : clearer error messages, especially when input file not present
-doc : clarified zstd_compression_format.md, by @ulikunitz
-misc: fixed zstdgrep, returns 1 on failure, by @lzutao
-misc: NEWS renamed as CHANGELOG, in accordance with fboss
-
-v1.3.7
-perf: slightly better decompression speed on clang (depending on hardware target)
-fix : performance of dictionary compression for small input < 4 KB at levels 9 and 10
-build: no longer build backtrace by default in release mode; restrict further automatic mode
-build: control backtrace support through build macro BACKTRACE
-misc: added man pages for zstdless and zstdgrep, by @samrussell
-
-v1.3.6
-perf: much faster dictionary builder, by @jenniferliu
-perf: faster dictionary compression on small data when using multiple contexts, by @felixhandte
-perf: faster dictionary decompression when using a very large number of dictionaries simultaneously
-cli : fix : does no longer overwrite destination when source does not exist (#1082)
-cli : new command --adapt, for automatic compression level adaptation
-api : fix : block api can be streamed with > 4 GB, reported by @catid
-api : reduced ZSTD_DDict size by 2 KB
-api : minimum negative compression level is defined, and can be queried using ZSTD_minCLevel().
-build: support Haiku target, by @korli
-build: Read Legacy format is limited to v0.5+ by default. Can be changed at compile time with macro ZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT.
-doc : zstd_compression_format.md updated to match wording in IETF RFC 8478
-misc: tests/paramgrill, a parameter optimizer, by @GeorgeLu97
-
-v1.3.5
-perf: much faster dictionary compression, by @felixhandte
-perf: small quality improvement for dictionary generation, by @terrelln
-perf: slightly improved high compression levels (notably level 19)
-mem : automatic memory release for long duration contexts
-cli : fix : overlapLog can be manually set
-cli : fix : decoding invalid lz4 frames
-api : fix : performance degradation for dictionary compression when using advanced API, by @terrelln
-api : change : clarify ZSTD_CCtx_reset() vs ZSTD_CCtx_resetParameters(), by @terrelln
-build: select custom libzstd scope through control macros, by @GeorgeLu97
-build: OpenBSD patch, by @bket
-build: make and make all are compatible with -j
-doc : clarify zstd_compression_format.md, updated for IETF RFC process
-misc: pzstd compatible with reproducible compilation, by @lamby
-
-v1.3.4
-perf: faster speed (especially decoding speed) on recent cpus (haswell+)
-perf: much better performance associating --long with multi-threading, by @terrelln
-perf: better compression at levels 13-15
-cli : asynchronous compression by default, for faster experience (use --single-thread for former behavior)
-cli : smoother status report in multi-threading mode
-cli : added command --fast=#, for faster compression modes
-cli : fix crash when not overwriting existing files, by Pádraig Brady (@pixelb)
-api : `nbThreads` becomes `nbWorkers` : 1 triggers asynchronous mode
-api : compression levels can be negative, for even more speed
-api : ZSTD_getFrameProgression() : get precise progress status of ZSTDMT anytime
-api : ZSTDMT can accept new compression parameters during compression
-api : implemented all advanced dictionary decompression prototypes
-build: improved meson recipe, by Shawn Landden (@shawnl)
-build: VS2017 scripts, by @HaydnTrigg
-misc: all /contrib projects fixed
-misc: added /contrib/docker script by @gyscos
-
-v1.3.3
-perf: faster zstd_opt strategy (levels 16-19)
-fix : bug #944 : multithreading with shared ditionary and large data, reported by @gsliepen
-cli : fix : content size written in header by default
-cli : fix : improved LZ4 format support, by @felixhandte
-cli : new : hidden command `-S`, to benchmark multiple files while generating one result per file
-api : fix : support large skippable frames, by @terrelln
-api : fix : streaming interface was adding a useless 3-bytes null block to small frames
-api : change : when setting `pledgedSrcSize`, use `ZSTD_CONTENTSIZE_UNKNOWN` macro value to mean "unknown"
-build: fix : compilation under rhel6 and centos6, reported by @pixelb
-build: added `check` target
-
-v1.3.2
-new : long range mode, using --long command, by Stella Lau (@stellamplau)
-new : ability to generate and decode magicless frames (#591)
-changed : maximum nb of threads reduced to 200, to avoid address space exhaustion in 32-bits mode
-fix : multi-threading compression works with custom allocators
-fix : ZSTD_sizeof_CStream() was over-evaluating memory usage
-fix : a rare compression bug when compression generates very large distances and bunch of other conditions (only possible at --ultra -22)
-fix : 32-bits build can now decode large offsets (levels 21+)
-cli : added LZ4 frame support by default, by Felix Handte (@felixhandte)
-cli : improved --list output
-cli : new : can split input file for dictionary training, using command -B#
-cli : new : clean operation artefact on Ctrl-C interruption
-cli : fix : do not change /dev/null permissions when using command -t with root access, reported by @mike155 (#851)
-cli : fix : write file size in header in multiple-files mode
-api : added macro ZSTD_COMPRESSBOUND() for static allocation
-api : experimental : new advanced decompression API
-api : fix : sizeof_CCtx() used to over-estimate
-build: fix : no-multithread variant compiles without pool.c dependency, reported by Mitchell Blank Jr (@mitchblank) (#819)
-build: better compatibility with reproducible builds, by Bernhard M. Wiedemann (@bmwiedemann) (#818)
-example : added streaming_memory_usage
-license : changed /examples license to BSD + GPLv2
-license : fix a few header files to reflect new license (#825)
-
-v1.3.1
-New license : BSD + GPLv2
-perf: substantially decreased memory usage in Multi-threading mode, thanks to reports by Tino Reichardt (@mcmilk)
-perf: Multi-threading supports up to 256 threads. Cap at 256 when more are requested (#760)
-cli : improved and fixed --list command, by @ib (#772)
-cli : command -vV to list supported formats, by @ib (#771)
-build : fixed binary variants, reported by @svenha (#788)
-build : fix Visual compilation for non x86/x64 targets, reported by Greg Slazinski (@GregSlazinski) (#718)
-API exp : breaking change : ZSTD_getframeHeader() provides more information
-API exp : breaking change : pinned down values of error codes
-doc : fixed huffman example, by Ulrich Kunitz (@ulikunitz)
-new : contrib/adaptive-compression, I/O driven compression strength, by Paul Cruz (@paulcruz74)
-new : contrib/long_distance_matching, statistics by Stella Lau (@stellamplau)
-updated : contrib/linux-kernel, by Nick Terrell (@terrelln)
-
-v1.3.0
-cli : new : `--list` command, by Paul Cruz
-cli : changed : xz/lzma support enabled by default
-cli : changed : `-t *` continue processing list after a decompression error
-API : added : ZSTD_versionString()
-API : promoted to stable status : ZSTD_getFrameContentSize(), by Sean Purcell
-API exp : new advanced API : ZSTD_compress_generic(), ZSTD_CCtx_setParameter()
-API exp : new : API for static or external allocation : ZSTD_initStatic?Ctx()
-API exp : added : ZSTD_decompressBegin_usingDDict(), requested by Guy Riddle (#700)
-API exp : clarified memory estimation / measurement functions.
-API exp : changed : strongest strategy renamed ZSTD_btultra, fastest strategy ZSTD_fast set to 1
-tools : decodecorpus can generate random dictionary-compressed samples, by Paul Cruz
-new : contrib/seekable_format, demo and API, by Sean Purcell
-changed : contrib/linux-kernel, updated version and license, by Nick Terrell
-
-v1.2.0
-cli : changed : Multithreading enabled by default (use target zstd-nomt or HAVE_THREAD=0 to disable)
-cli : new : command -T0 means "detect and use nb of cores", by Sean Purcell
-cli : new : zstdmt symlink hardwired to `zstd -T0`
-cli : new : command --threads=# (#671)
-cli : changed : cover dictionary builder by default, for improved quality, by Nick Terrell
-cli : new : commands --train-cover and --train-legacy, to select dictionary algorithm and parameters
-cli : experimental targets `zstd4` and `xzstd4`, with support for lz4 format, by Sean Purcell
-cli : fix : does not output compressed data on console
-cli : fix : ignore symbolic links unless --force specified,
-API : breaking change : ZSTD_createCDict_advanced(), only use compressionParameters as argument
-API : added : prototypes ZSTD_*_usingCDict_advanced(), for direct control over frameParameters.
-API : improved: ZSTDMT_compressCCtx() reduced memory usage
-API : fix : ZSTDMT_compressCCtx() now provides srcSize in header (#634)
-API : fix : src size stored in frame header is controlled at end of frame
-API : fix : enforced consistent rules for pledgedSrcSize==0 (#641)
-API : fix : error code "GENERIC" replaced by "dstSizeTooSmall" when appropriate
-build: improved cmake script, by @Majlen
-build: enabled Multi-threading support for *BSD, by Baptiste Daroussin
-tools: updated Paramgrill. Command -O# provides best parameters for sample and speed target.
-new : contrib/linux-kernel version, by Nick Terrell
-
-v1.1.4
-cli : new : can compress in *.gz format, using --format=gzip command, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-cli : new : advanced benchmark command --priority=rt
-cli : fix : write on sparse-enabled file systems in 32-bits mode, by @ds77
-cli : fix : --rm remains silent when input is stdin
-cli : experimental : xzstd, with support for xz/lzma decoding, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-speed : improved decompression speed in streaming mode for single shot scenarios (+5%)
-memory: DDict (decompression dictionary) memory usage down from 150 KB to 20 KB
-arch: 32-bits variant able to generate and decode very long matches (>32 MB), by Sean Purcell
-API : new : ZSTD_findFrameCompressedSize(), ZSTD_getFrameContentSize(), ZSTD_findDecompressedSize()
-API : changed : dropped support of legacy versions <= v0.3 (can be changed by modifying ZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT value)
-build : new: meson build system in contrib/meson, by Dima Krasner
-build : improved cmake script, by @Majlen
-build : added -Wformat-security flag, as recommended by Padraig Brady
-doc : new : educational decoder, by Sean Purcell
-
-v1.1.3
-cli : zstd can decompress .gz files (can be disabled with `make zstd-nogz` or `make HAVE_ZLIB=0`)
-cli : new : experimental target `make zstdmt`, with multi-threading support
-cli : new : improved dictionary builder "cover" (experimental), by Nick Terrell, based on prior work by Giuseppe Ottaviano.
-cli : new : advanced commands for detailed parameters, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-cli : fix zstdless on Mac OS-X, by Andrew Janke
-cli : fix #232 "compress non-files"
-dictBuilder : improved dictionary generation quality, thanks to Nick Terrell
-API : new : lib/compress/ZSTDMT_compress.h multithreading API (experimental)
-API : new : ZSTD_create?Dict_byReference(), requested by Bartosz Taudul
-API : new : ZDICT_finalizeDictionary()
-API : fix : ZSTD_initCStream_usingCDict() properly writes dictID into frame header, by Gregory Szorc (#511)
-API : fix : all symbols properly exposed in libzstd, by Nick Terrell
-build : support for Solaris target, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-doc : clarified specification, by Sean Purcell
-
-v1.1.2
-API : streaming : decompression : changed : automatic implicit reset when chain-decoding new frames without init
-API : experimental : added : dictID retrieval functions, and ZSTD_initCStream_srcSize()
-API : zbuff : changed : prototypes now generate deprecation warnings
-lib : improved : faster decompression speed at ultra compression settings and 32-bits mode
-lib : changed : only public ZSTD_ symbols are now exposed
-lib : changed : reduced usage of stack memory
-lib : fixed : several corner case bugs, by Nick Terrell
-cli : new : gzstd, experimental version able to decode .gz files, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-cli : new : preserve file attributes
-cli : new : added zstdless and zstdgrep tools
-cli : fixed : status displays total amount decoded, even for file consisting of multiple frames (like pzstd)
-cli : fixed : zstdcat
-zlib_wrapper : added support for gz* functions, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-install : better compatibility with FreeBSD, by Dimitry Andric
-source tree : changed : zbuff source files moved to lib/deprecated
-
-v1.1.1
-New : command -M#, --memory=, --memlimit=, --memlimit-decompress= to limit allowed memory consumption
-New : doc/zstd_manual.html, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-Improved : slightly better compression ratio at --ultra levels (>= 20)
-Improved : better memory usage when using streaming compression API, thanks to @Rogier-5 report
-Added : API : ZSTD_initCStream_usingCDict(), ZSTD_initDStream_usingDDict() (experimental section)
-Added : example/multiple_streaming_compression.c
-Changed : zstd_errors.h is now installed within /include (and replaces errors_public.h)
-Updated man page
-Fixed : zstd-small, zstd-compress and zstd-decompress compilation targets
-
-v1.1.0
-New : contrib/pzstd, parallel version of zstd, by Nick Terrell
-added : NetBSD install target (#338)
-Improved : speed for batches of small files
-Improved : speed of zlib wrapper, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-Changed : libzstd on Windows supports legacy formats, by Christophe Chevalier
-Fixed : CLI -d output to stdout by default when input is stdin (#322)
-Fixed : CLI correctly detects console on Mac OS-X
-Fixed : CLI supports recursive mode `-r` on Mac OS-X
-Fixed : Legacy decoders use unified error codes, reported by benrg (#341), fixed by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-Fixed : compatibility with OpenBSD, reported by Juan Francisco Cantero Hurtado (#319)
-Fixed : compatibility with Hurd, by Przemyslaw Skibinski (#365)
-Fixed : zstd-pgo, reported by octoploid (#329)
-
-v1.0.0
-Change Licensing, all project is now BSD, Copyright Facebook
-Small decompression speed improvement
-API : Streaming API supports legacy format
-API : ZDICT_getDictID(), ZSTD_sizeof_{CCtx, DCtx, CStream, DStream}(), ZSTD_setDStreamParameter()
-CLI supports legacy formats v0.4+
-Fixed : compression fails on certain huge files, reported by Jesse McGrew
-Enhanced documentation, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-
-v0.8.1
-New streaming API
-Changed : --ultra now enables levels beyond 19
-Changed : -i# now selects benchmark time in second
-Fixed : ZSTD_compress* can now compress > 4 GB in a single pass, reported by Nick Terrell
-Fixed : speed regression on specific patterns (#272)
-Fixed : support for Z_SYNC_FLUSH, by Dmitry Krot (#291)
-Fixed : ICC compilation, by Przemyslaw Skibinski
-
-v0.8.0
-Improved : better speed on clang and gcc -O2, thanks to Eric Biggers
-New : Build on FreeBSD and DragonFly, thanks to JrMarino
-Changed : modified API : ZSTD_compressEnd()
-Fixed : legacy mode with ZSTD_HEAPMODE=0, by Christopher Bergqvist
-Fixed : premature end of frame when zero-sized raw block, reported by Eric Biggers
-Fixed : large dictionaries (> 384 KB), reported by Ilona Papava
-Fixed : checksum correctly checked in single-pass mode
-Fixed : combined --test amd --rm, reported by Andreas M. Nilsson
-Modified : minor compression level adaptations
-Updated : compression format specification to v0.2.0
-changed : zstd.h moved to /lib directory
-
-v0.7.5
-Transition version, supporting decoding of v0.8.x
-
-v0.7.4
-Added : homebrew for Mac, by Daniel Cade
-Added : more examples
-Fixed : segfault when using small dictionaries, reported by Felix Handte
-Modified : default compression level for CLI is now 3
-Updated : specification, to v0.1.1
-
-v0.7.3
-New : compression format specification
-New : `--` separator, stating that all following arguments are file names. Suggested by Chip Turner.
-New : `ZSTD_getDecompressedSize()`
-New : OpenBSD target, by Juan Francisco Cantero Hurtado
-New : `examples` directory
-fixed : dictBuilder using HC levels, reported by Bartosz Taudul
-fixed : legacy support from ZSTD_decompress_usingDDict(), reported by Felix Handte
-fixed : multi-blocks decoding with intermediate uncompressed blocks, reported by Greg Slazinski
-modified : removed "mem.h" and "error_public.h" dependencies from "zstd.h" (experimental section)
-modified : legacy functions no longer need magic number
-
-v0.7.2
-fixed : ZSTD_decompressBlock() using multiple consecutive blocks. Reported by Greg Slazinski.
-fixed : potential segfault on very large files (many gigabytes). Reported by Chip Turner.
-fixed : CLI displays system error message when destination file cannot be created (#231). Reported by Chip Turner.
-
-v0.7.1
-fixed : ZBUFF_compressEnd() called multiple times with too small `dst` buffer, reported by Christophe Chevalier
-fixed : dictBuilder fails if first sample is too small, reported by Руслан Ковалёв
-fixed : corruption issue, reported by cj
-modified : checksum enabled by default in command line mode
-
-v0.7.0
-New : Support for directory compression, using `-r`, thanks to Przemyslaw Skibinski
-New : Command `--rm`, to remove source file after successful de/compression
-New : Visual build scripts, by Christophe Chevalier
-New : Support for Sparse File-systems (do not use space for zero-filled sectors)
-New : Frame checksum support
-New : Support pass-through mode (when using `-df`)
-API : more efficient Dictionary API : `ZSTD_compress_usingCDict()`, `ZSTD_decompress_usingDDict()`
-API : create dictionary files from custom content, by Giuseppe Ottaviano
-API : support for custom malloc/free functions
-New : controllable Dictionary ID
-New : Support for skippable frames
-
-v0.6.1
-New : zlib wrapper API, thanks to Przemyslaw Skibinski
-New : Ability to compile compressor / decompressor separately
-Changed : new lib directory structure
-Fixed : Legacy codec v0.5 compatible with dictionary decompression
-Fixed : Decoder corruption error (#173)
-Fixed : null-string roundtrip (#176)
-New : benchmark mode can select directory as input
-Experimental : midipix support, VMS support
-
-v0.6.0
-Stronger high compression modes, thanks to Przemyslaw Skibinski
-API : ZSTD_getFrameParams() provides size of decompressed content
-New : highest compression modes require `--ultra` command to fully unleash their capacity
-Fixed : zstd cli return error code > 0 and removes dst file artifact when decompression fails, thanks to Chip Turner
-
-v0.5.1
-New : Optimal parsing => Very high compression modes, thanks to Przemyslaw Skibinski
-Changed : Dictionary builder integrated into libzstd and zstd cli
-Changed (!) : zstd cli now uses "multiple input files" as default mode. See `zstd -h`.
-Fix : high compression modes for big-endian platforms
-New : zstd cli : `-t` | `--test` command
-
-v0.5.0
-New : dictionary builder utility
-Changed : streaming & dictionary API
-Improved : better compression of small data
-
-v0.4.7
-Improved : small compression speed improvement in HC mode
-Changed : `zstd_decompress.c` has ZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT to 0 by default
-fix : bt search bug
-
-v0.4.6
-fix : fast compression mode on Windows
-New : cmake configuration file, thanks to Artyom Dymchenko
-Improved : high compression mode on repetitive data
-New : block-level API
-New : ZSTD_duplicateCCtx()
-
-v0.4.5
-new : -m/--multiple : compress/decompress multiple files
-
-v0.4.4
-Fixed : high compression modes for Windows 32 bits
-new : external dictionary API extended to buffered mode and accessible through command line
-new : windows DLL project, thanks to Christophe Chevalier
-
-v0.4.3 :
-new : external dictionary API
-new : zstd-frugal
-
-v0.4.2 :
-Generic minor improvements for small blocks
-Fixed : big-endian compatibility, by Peter Harris (#85)
-
-v0.4.1
-Fixed : ZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT=0 build mode (reported by Luben)
-removed `zstd.c`
-
-v0.4.0
-Command line utility compatible with high compression levels
-Removed zstdhc => merged into zstd
-Added : ZBUFF API (see zstd_buffered.h)
-Rolling buffer support
-
-v0.3.6
-small blocks params
-
-v0.3.5
-minor generic compression improvements
-
-v0.3.4
-Faster fast cLevels
-
-v0.3.3
-Small compression ratio improvement
-
-v0.3.2
-Fixed Visual Studio
-
-v0.3.1 :
-Small compression ratio improvement
-
-v0.3
-HC mode : compression levels 2-26
-
-v0.2.2
-Fix : Visual Studio 2013 & 2015 release compilation, by Christophe Chevalier
-
-v0.2.1
-Fix : Read errors, advanced fuzzer tests, by Hanno Böck
-
-v0.2.0
-**Breaking format change**
-Faster decompression speed
-Can still decode v0.1 format
-
-v0.1.3
-fix uninitialization warning, reported by Evan Nemerson
-
-v0.1.2
-frame concatenation support
-
-v0.1.1
-fix compression bug
-detects write-flush errors
-
-v0.1.0
-first release
+++ /dev/null
- **Zstd**, short for Zstandard, is a fast lossless compression algorithm,
- targeting real-time compression scenarios at zlib-level and better compression ratios.
-
-It is provided as an open-source BSD-licensed **C** library.
-For other programming languages,
-you can consult a list of known ports on [Zstandard homepage](http://www.zstd.net/#other-languages).
-
-|Branch |Status |
-|------------|---------|
-|master | [](https://travis-ci.org/facebook/zstd) |
-|dev | [](https://travis-ci.org/facebook/zstd) |
-
-As a reference, several fast compression algorithms were tested and compared on a Core i7-3930K CPU @ 4.5GHz, using [lzbench], an open-source in-memory benchmark by @inikep compiled with gcc 5.4.0, with the [Silesia compression corpus].
-
-[lzbench]: https://github.com/inikep/lzbench
-[Silesia compression corpus]: http://sun.aei.polsl.pl/~sdeor/index.php?page=silesia
-
-
-|Name | Ratio | C.speed | D.speed |
-|-----------------|-------|--------:|--------:|
-| | | MB/s | MB/s |
-|**zstd 0.8.2 -1**|**2.877**|**330**| **940** |
-| [zlib] 1.2.8 -1 | 2.730 | 95 | 360 |
-| brotli 0.4 -0 | 2.708 | 320 | 375 |
-| QuickLZ 1.5 | 2.237 | 510 | 605 |
-| LZO 2.09 | 2.106 | 610 | 870 |
-| [LZ4] r131 | 2.101 | 620 | 3100 |
-| Snappy 1.1.3 | 2.091 | 480 | 1600 |
-| LZF 3.6 | 2.077 | 375 | 790 |
-
-[zlib]:http://www.zlib.net/
-[LZ4]: http://www.lz4.org/
-
-Zstd can also offer stronger compression ratios at the cost of compression speed.
-Speed vs Compression trade-off is configurable by small increment. Decompression speed is preserved and remain roughly the same at all settings, a property shared by most LZ compression algorithms, such as [zlib] or lzma.
-
-The following tests were run on a Core i7-3930K CPU @ 4.5GHz, using [lzbench], an open-source in-memory benchmark by @inikep compiled with gcc 5.2.1, on the [Silesia compression corpus].
-
-Compression Speed vs Ratio | Decompression Speed
----------------------------|--------------------
- | 
-
-Several algorithms can produce higher compression ratio but at slower speed, falling outside of the graph.
-For a larger picture including very slow modes, [click on this link](images/DCspeed5.png) .
-
-
-### The case for Small Data compression
-
-Previous charts provide results applicable to typical files and streams scenarios (several MB). Small data come with different perspectives. The smaller the amount of data to compress, the more difficult it is to achieve any significant compression.
-
-This problem is common to any compression algorithm. The reason is, compression algorithms learn from past data how to compress future data. But at the beginning of a new file, there is no "past" to build upon.
-
-To solve this situation, Zstd offers a __training mode__, which can be used to tune the algorithm for a selected type of data, by providing it with a few samples. The result of the training is stored in a file called "dictionary", which can be loaded before compression and decompression. Using this dictionary, the compression ratio achievable on small data improves dramatically :
-
-
-
-These compression gains are achieved while simultaneously providing faster compression and decompression speeds.
-
-Dictionary work if there is some correlation in a family of small data (there is no _universal dictionary_).
-Hence, deploying one dictionary per type of data will provide the greater benefits. Dictionary gains are mostly effective in the first few KB. Then, the compression algorithm will rely more and more on previously decoded content to compress the rest of the file.
-
-#### Dictionary compression How To :
-
-1) Create the dictionary
-
-`zstd --train FullPathToTrainingSet/* -o dictionaryName`
-
-2) Compress with dictionary
-
-`zstd FILE -D dictionaryName`
-
-3) Decompress with dictionary
-
-`zstd --decompress FILE.zst -D dictionaryName`
-
-### Status
-
-Zstandard is currently deployed within Facebook. It is used daily to compress and decompress very large amount of data in multiple formats and use cases.
-Zstandard is considered safe for production environments.
-
-### License
-
-Zstandard is [BSD-licensed](LICENSE). We also provide an [additional patent grant](PATENTS).
-
-### Contributing
-
-The "dev" branch is the one where all contributions will be merged before reaching "master".
-If you plan to propose a patch, please commit into the "dev" branch or its own feature branch.
-Direct commit to "master" are not permitted.
-For more information, please read [CONTRIBUTING](CONTRIBUTING.md).
-
-### Miscellaneous
-
-Zstd entropy stage is provided by [Huff0 and FSE, from Finite State Entropy library](https://github.com/Cyan4973/FiniteStateEntropy).